| Previous | Contents | Index |
Figure 3-6 shows sample OpenVMS CPU Mode Summary and CPU Process States, which are the left and right top panes of the CPU Modes page.
Figure 3-6 OpenVMS CPU Mode Summary and Process States
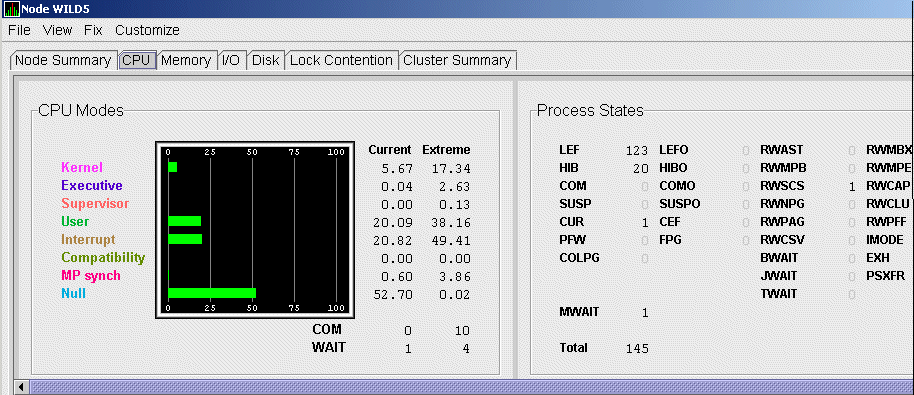
In the CPU Mode Summary section of the pane, percentages are averaged across all the CPUs and are displayed as a single value on symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) nodes.
To the left of the graph is a list of CPU modes. The bars in the graph represent the percentage of CPU cycles used for each mode. To the right of the graph are current and extreme percentages of time spent in each mode.
Below the graph, the Availability Manager displays the COM and WAIT process queues:
The right side of Figure 3-6 shows a sample CPU Process States display. Note that the value for MWAIT, in the left column, is the sum of all values for the states in the two right columns.
This display shows the number of processes in each process state. This number is tallied from the data in CPU Process view of the CPU page (Figure 3-6). For systems with many processes, the data in the CPU Process view is collected in segments over a short period of time because the amount of data a network packet can contain is limited. Because of this, the number of processes in the Process States pane might differ slightly from what is reported in $MONITOR STATES.
Appendix A contains explanations of the CPU process states.
3.2.2.3 OpenVMS CPU Mode Details
The lower pane of the CPU Modes page contains CPU mode details, as shown in Figure 3-7.
Figure 3-7 OpenVMS CPU Mode Details Pane

In the OpenVMS CPU Mode Details pane, the following data is displayed:
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU ID | Decimal value representing the identity of a processor in a multiprocessing system. On a uniprocessor, this value is always CPU #00. |
| State | One of the following CPU states: Boot, Booted, Init, Rejected, Reserved, Run, Stopped, Stopping, or Timeout. |
| Mode % | Graphical representation of the percentage of active modes on that CPU. The color displayed coincides with the mode color in the graph in the top pane. |
| PID | Process identifier (PID) value of the process that is using the CPU. If the PID is unknown to the Data Analyzer application, the internal PID (IPID) is listed. |
| Process Name | Name of the process active on the CPU. If no active process is found on the CPU, the name is listed as *** None ***. |
| Capabilities |
One or more of the following CPU capabilities or flags:
|
| RAD | Number of the RAD where the CPU exists. |
To display the OpenVMS CPU Process Summary pane at the bottom of the CPU page, select CPU Process Summary from the View menu (Figure 3-6). Figure 3-8 shows a sample OpenVMS CPU Process Summary pane.
Figure 3-8 OpenVMS CPU Process Summary Pane
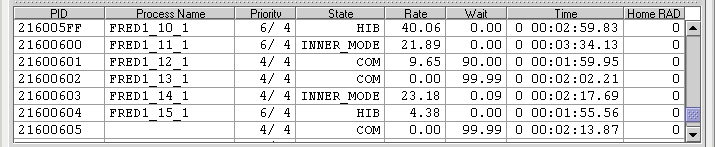
The OpenVMS CPU Process Summary pane displays the following data:
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| PID | Process identifier, a 32-bit value that uniquely identifies a process. |
| Process Name | Name of the process active on the CPU. |
| Priority | Computable (xx) and base (yy) process priority in the format xx/yy. |
| State | One of the process states listed in Appendix A. |
| Rate | Percentage of CPU time used by this process. This is the ratio of CPU time to elapsed time. The CPU rate is also displayed in the bar graph. |
| Wait | Percentage of time the process is in the COM or COMO state. |
| Time | Amount of actual CPU time charged to the process. |
| Home RAD | Where most of the resources of the process reside. |
Displaying Single Process Information
When you double-click a PID on the lower part of an OpenVMS CPU Process Summary (Figure 3-8), Memory Summary (Figure 3-10), or I/O Summary (Figure 3-12) page, the Availability Manager displays the first of several OpenVMS Single Process pages.
On these pages, you can click tabs to display specific data about one process. Alternatively, you can display all of the information on the pages on a single vertical or horizontal grid page.
This data includes a combination of data elements from the CPU Process,
Memory, and I/O pages, as well as data for specific quota utilization,
current image, and queue wait time. These pages are described in more
detail in Section 3.3.
3.2.3 Memory Summaries and Details
The Memory Summary and Memory Details pages contain statistics about
memory usage on the node you select.
The Memory Summary pages displayed for OpenVMS and Windows nodes are
somewhat different, as described in the following sections. The Memory
Details page exists only for OpenVMS systems.
3.2.3.1 Windows Memory Summary
To display the Windows Memory Summary page, you can use either of the following methods:
The Availability Manager displays the Windows Memory page (Figure 3-9).
Figure 3-9 Windows Memory
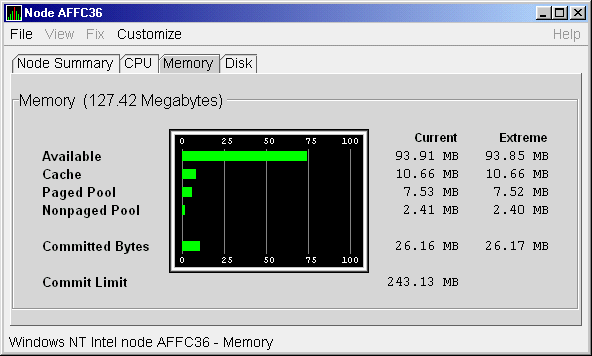
The Current and Extreme amounts on the page display the data shown in the following table. The table also indicates what the graph amounts represent.
When you double-click a value under the MEM heading in an OpenVMS Node pane, or if you click the Memory tab, the Availability Manager displays the OpenVMS Memory Summary page (Figure 3-10).
Alternatively, if you click the View menu on the OpenVMS Memory Summary page, the following options are displayed in a shortcut menu:
You can click Memory Summary View to select the Memory Summary page.
Figure 3-10 OpenVMS Memory Summary
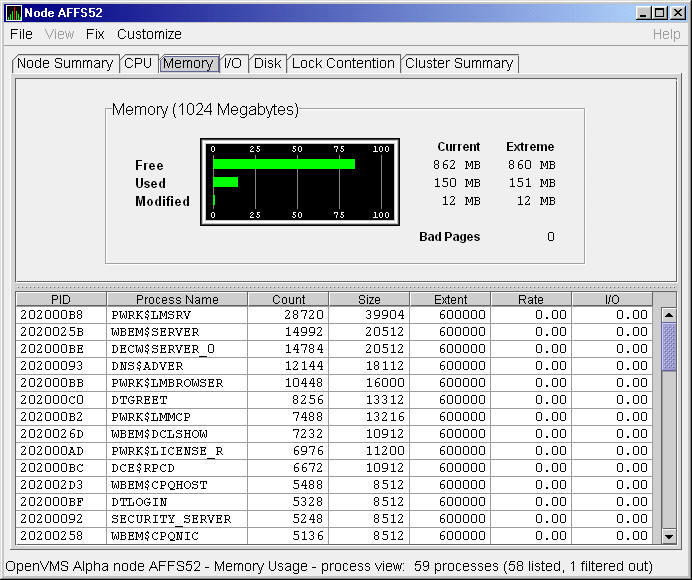
The graph in the top pane of Figure 3-10 shows memory distribution (Free, Used, and Modified) as absolute values, in megabytes of memory. Current and extreme values are also listed for each type of memory distribution. (Free memory uses the lowest seen value as its extreme.) Bad Pages show the number of pages that the operating system has marked as bad.
The thresholds that you see in the graph are the ones set for the LOMEMY event. (The LOMEMY thresholds are also in the display of values for the MEM field in the OpenVMS Group/Node pane shown in Figure 2-1.)
The lower pane in Figure 3-10 displays the data shown in the following table, including an abbreviation of the event that is related to each type of data, where applicable.
| Data | Description | Related Events |
|---|---|---|
| PID | Process identifier. A 32-bit value that uniquely identifies a process. | n/a |
| Process Name | Name of the process. |
NOPROC,
PRCFND |
| Count | Number of physical pages or pagelets of memory that the process is using for the working set count. | LOWEXT |
| Size | Number of pages or pagelets of memory the process is allowed to use for the working set size (also known as the working set list size). The operating system periodically adjusts this value based on an analysis of page faults relative to CPU time used. | LOWSQU |
| Extent | Number of pages or pagelets of memory in the process's working set extent (WSEXTENT) quota as defined in the user authorization file (UAF). Number of pages or pagelets cannot exceed the value of the system parameter WSMAX. | LOWEXT |
| Rate | Number of page faults per second for the process. |
LOWSQU,
LOWEXT, PRPGFL |
| I/O | Rate of I/O read attempts necessary to satisfy page faults (also known as page read I/O or the hard fault rate). | PRPIOR |
When you double-click a PID on the lower part of the Memory Summary
page (Figure 3-10), the Availability Manager displays an OpenVMS Single
Process (Figure 3-23), where you can click tabs to display pages
containing specific data about one process. This data includes a
combination of data from the CPU Process, Memory, and I/O pages, as
well as data for specific quota utilization, current image, and queue
wait time. These pages are described in Section 3.3.
3.2.3.3 OpenVMS Memory Details
When you click the View menu on the OpenVMS Memory Summary page (Figure 3-10), the following options are displayed in a shortcut menu. To display memory details, select that option.
The Availability Manager displays the OpenVMS Memory Details page (Figure 3-11).
Figure 3-11 OpenVMS Memory Details
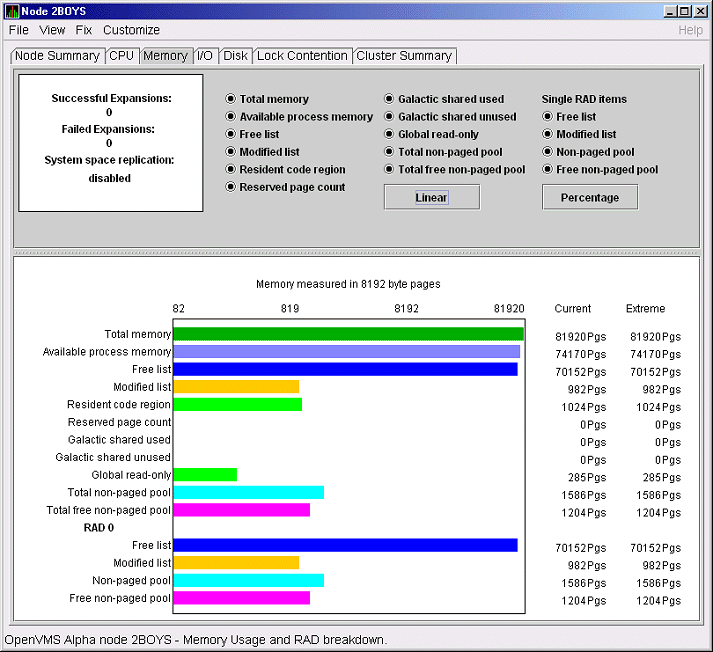
The following data items are in a box at the top left of the page:
| Heading | Description |
|---|---|
| Successful Expansions | Number of successful nonpaged pool expansions. |
| Failed Expansions | Number of failed attempts to expand nonpaged pool. |
| System space replication | Whether system space replication is enabled or disabled. |
To the right of the box is a list of system memory data that is displayed in the bar graphs at the bottom of the page. You can toggle these data items on or off (that is, to display them as bar graphs). You can also click a small box to choose between Linear and Logarithmic bar graph displays.
The system memory data items are described in Table 3-5.
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Total memory | Total physical memory size, as seen by OpenVMS. |
| Available process memory | Amount of total physical memory available to processes. This is the total memory minus memory allocated to OpenVMS. |
| Free list | Size of the free page list. |
| Modified list | Size of the modified page list. |
| Resident code region | Size of the resident image code region. |
| Reserved page count | Number of reserved memory pages. |
| Galactic shared used | Galaxy shared memory pages currently in use. |
| Galactic shared unused | Galaxy shared memory pages currently not in use. |
| Global read-only | Read-only pages, which are installed as resident when system space replication is enabled, that will also be replicated for improved performance. |
| Total nonpaged pool | Total size of system nonpaged pool. |
| Total free nonpaged pool | Amount of nonpaged pool that is currently free. |
To the right of the system memory data is a list of single RAD data items, which are described in Section 3.3.7. You can toggle these items to display them in bar graphs.
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Free list | Size of the free page list. |
| Modified list | Size of the modified page list. |
| Nonpaged pool | Total size of system nonpaged pool. |
| Free nonpaged pool | Amount of nonpaged pool that is currently free. |
Below the list of single RAD items is a box where you can toggle
between Percentage and Raw Data to display Current and Extreme values
to the right of the bar graphs.
3.2.4 OpenVMS I/O Summary and Page/Swap Files
By clicking the I/O tab on any OpenVMS node data page, you can display a page that contains summaries of accumulated I/O rates. In the top pane, the summary covers all processes; in the lower pane, the summary is for one process.
From the View menu, you can also choose to display (in the lower pane)
a list of page and swap files.
3.2.4.1 OpenVMS I/O Summary
The OpenVMS I/O Summary page displays the rate, per second, at which I/O transfers take place, including paging write I/O (WIO), direct I/O (DIO), and buffered I/O (BIO). In the top pane, the summary is for all CPUs; in the lower pane, the summary is for one process.
When you double-click a data item under the DIO or BIO heading on the Node pane, or if you click the I/O tab, the Availability Manager displays, by default, the OpenVMS I/O Summary (Figure 3-12).
Figure 3-12 OpenVMS I/O Summary
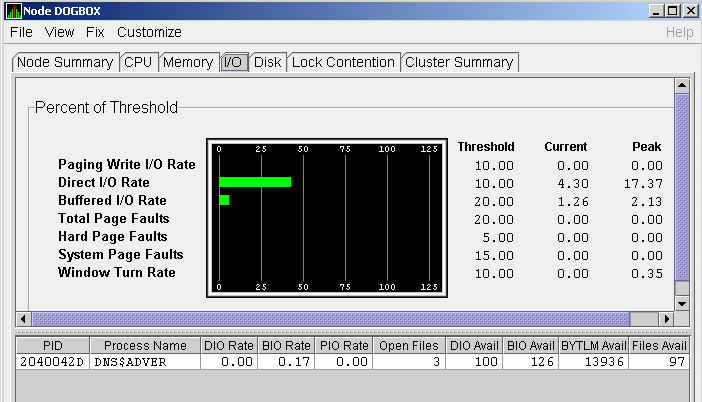
The graph in the top pane represents the percentage of thresholds for the types of I/O shown in Table 3-7. The table also shows the event that is related to each data item. For information about setting event thresholds, see Section 7.8.)
| Type of I/O | I/O Description | Related Event |
|---|---|---|
| Paging Write I/O Rate | Rate of write I/Os to one or more paging files. | HIPWIO |
| Direct I/O Rate | Transfers are from the pages or pagelets containing the process buffer that the system locks in physical memory to the system devices. | HIDIOR |
| Buffered I/O Rate | Transfers are for the process buffer from an intermediate buffer from the system buffer pool. | HIBIOR |
| Total Page Faults | Total of hard and soft page faults on the system, as well as peak values seen during an Availability Manager session. | HITTLP |
| Hard Page Faults | Total of hard page faults on the system. | HIHRDP |
| System Page Faults | Page faults generated by OpenVMS itself. | HISYSP |
| Window Turn Rate | Number of times that the file extent cache had to be refreshed. | WINTRN |
Current and peak values are listed for each type of I/O. Values that exceed thresholds set by the events indicated in the table are displayed in red on the screen. Appendix B describes OpenVMS and Windows events.
To the right of the graph, the following values are listed:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Threshold | Defined in Event Configuration Properties. |
| Current | Current value or rate. |
| Peak | Highest value or rate seen since start of data collection. |
The lower pane displays summary accumulated I/O rates on a per-process basis. The following data is displayed:
When you double-click a PID on the lower part of the I/O Summary page, the Availability Manager displays an OpenVMS Single Process, where you can click tabs to display specific data about one process. See Section 3.3 for more details.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |