![[Compaq]](../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 30 March 2001 | |
![[Compaq]](../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
DECamds displays them in the Event Log window. Node is replaced by the name of the node to which the event is related. Process is replaced by the name of the process to which the event is related.
LOASTQ, node process has used most of its ASTLM process quota
LOBIOQ, node process has used most of its BIOLM process quota
LOBYTQ, node process has used most of its BYTLM job quota
LODIOQ, node process has used most of its DIOLM process quota
LOENQU, node process has used most of its ENQLM job quota
LOFILQ, node process has used most of its FILLM job quota
LOPGFQ, node process has used most of its PGFLQUOTA job quota
LOPRCQ, node process has used most of its PRCLM process quota
LOTQEQ, node process has used most of its TQELM job quota
LOWEXT, node process working set extent is too small
LOWSQU, node process working set quota is too small
PRBIOR, node process buffered I/O rate is high
PRBIOW, node process waiting for buffered I/O
PRCCOM, node process waiting in COM or COMO
PRCCUR, node process has high CPU rate
PRCMUT, node process waiting for a mutex
PRCPUL, node process has used most of its CPUTIME process quota
PRCPWT, node process waiting in COLPG, PFW, or FPG
PRCQUO, node process waiting for a quota
PRCRWA, node process waiting in RWAST
PRCRWC, node process waiting in RWCAP
PRCRWM, node process waiting in RWMBX
PRCRWP, node process waiting in RWPAG, PWNPG, RWMPE, or RWMPB
PRCRWS, node process waiting in RWSCS, RWCLU, or RWCSV
PRCUNK, node process waiting for a system resource
PRDIOR, node process direct I/O rate is high
PRDIOW, node process waiting for direct I/O
PRLCKW, node process waiting for a lock
PRPGFL, node process high page fault rate
PRPIOR, node process paging I/O rate is high
3.11 Lock Contention Summary Window
The Lock Contention Summary window shown in Figure 3-12 determines
which resources are under contention. It displays all the OpenVMS Lock
Manager resources that have potential lock contention situations. The
Lock Contention Summary window is available only for groups; attempting
to open a Lock Contention Summary for a node opens the node's group
window.
Figure 3-12 Lock Contention Summary Window
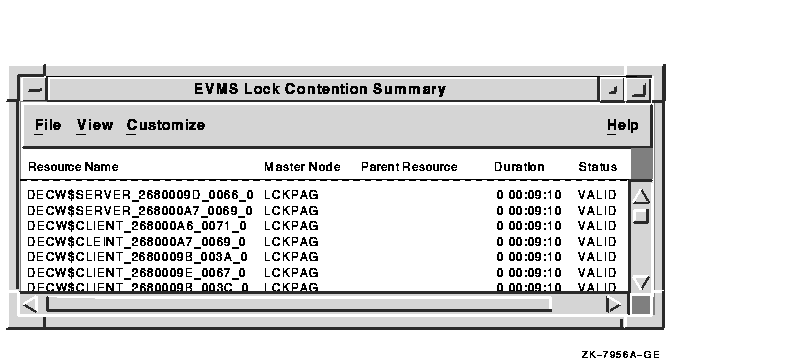
Locks are written to AMDS$LOCK_LOG.LOG; see Section B.3 for more information. To interpret the information displayed in the Lock Contention Summary window, you should have an understanding of OpenVMS lock management services. For more information, see the OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual.
Lock contention data is accurate only if every node in an OpenVMS Cluster environment is in the same group. Multiple clusters can share a group, but clusters cannot be divided into different groups without losing accuracy. |
You can open a Lock Contention Summary window from the Event Log or System Overview windows, as follows:
Table 3-12 describes the Lock Contention Summary window data fields.
| Field | Displays |
|---|---|
| Resource Name | The resource name associated with the $ENQ system service call. |
| Master Node | The node on which the resource is mastered. |
| Parent Resource | The name of the parent resource. If no name is displayed, the resource listed is the parent resource. |
| Duration | The amount of time elapsed since DECamds first detected the contention situation. |
| Status | The status of the lock. See the $ENQ(W) description in the OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual. |
You can open a Single Lock Summary window from the Lock Contention Summary window. See Section 3.12 for more information.
Figure 3-13 shows how to determine which filters can or cannot be displayed. To filter specific locks from the display, choose Filter Data... from the Customize menu on the Lock Contention Summary window. A filter dialog box appears with a list of locks currently being filtered from the display.
To add a filter, use either of the following methods:
Figure 3-13 Filtering Lock Events
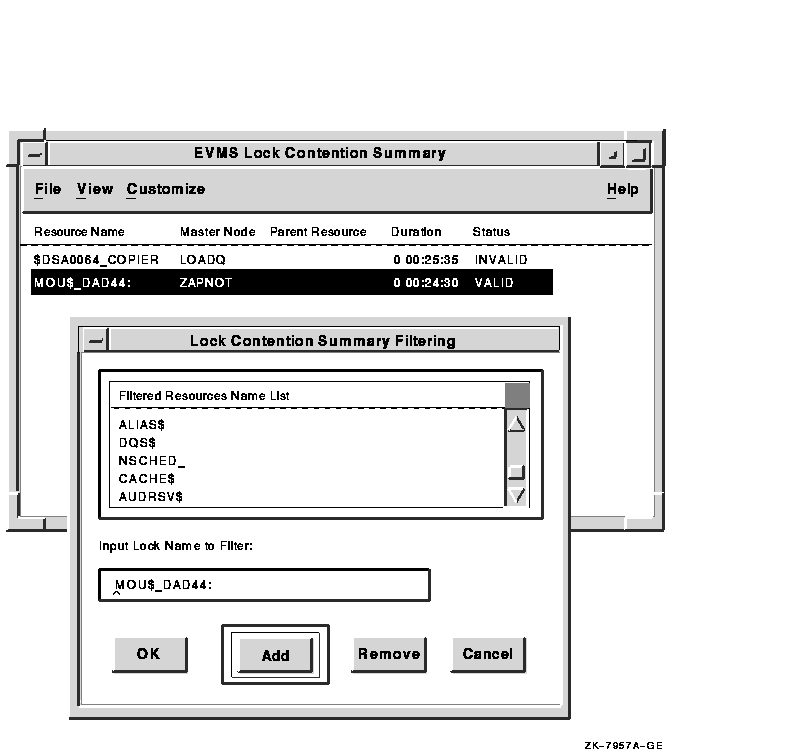
You can remove a lock from the filter list by selecting a lock and clicking on the Remove button. Any lock contentions affected by the removed filter will be displayed.
DECamds detects the following lock contention-related events and displays them in the Event Log window. Italicized words are replaced with actual values.
LCKCNT, node possible contention for resource resource
LRGHSH, node lock hash table too large n entries
RESDNS, node resource hash table dense percentage full n resources, hash table size n
RESPRS, node resource hash table sparse, only percentage full n resources, table size n
3.12 Single Lock Summary Window
The Single Lock Summary window shown in Figure 3-14 displays data
about a blocking lock and all locks in the granted, conversion, and
waiting queues. You can use it to display detailed information about a
lock contention situation. The lock name is specified in the title bar.
All locks are written to AMDS$LOCK_LOG.LOG; see Section B.3 for more
information.
Figure 3-14 Single Lock Summary Window
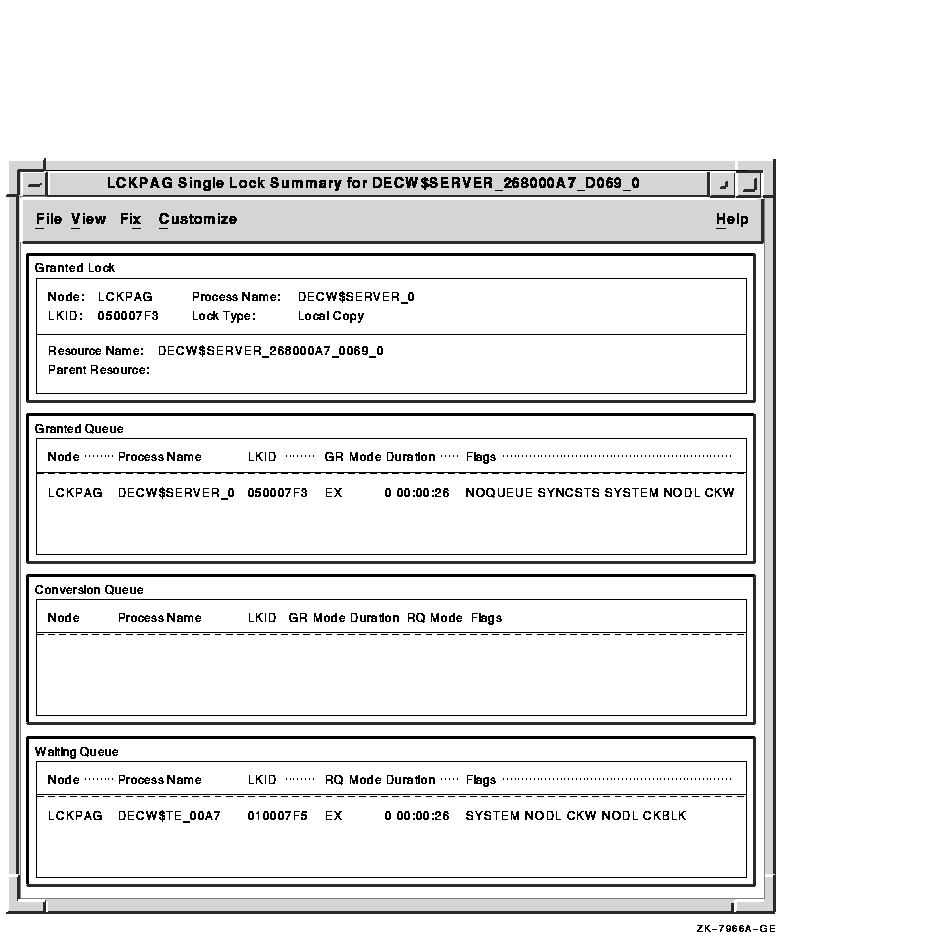
In a Single Lock Summary window, if DECamds cannot determine the node name for the group, it uses the cluster system ID (CSID) value, which the OpenVMS Cluster software uses to uniquely identify cluster members.
To open a Single Lock Summary window, do one of the following:
Table 3-13 describes the Single Lock Summary window data fields.
| Field | Displays |
|---|---|
| Granted Lock | |
| Node | The node name on which the lock is granted. |
| LKID | The lock ID value (which is useful with SDA). |
| Process Name | The name of the process owning the blocking lock. |
| Lock Type | One of the following: Local Copy, Process Copy, or Master Copy. |
| Resource Name | The name of the resource. |
| Parent Resource | The name of the parent resource (if any). |
| Granted, Conversion, and Waiting Queue | |
| Node | The node on which the lock block resides. |
| Process Name | The process name of the process owning the lock. |
| LKID | The lock ID value (which is useful with SDA). |
| GR Mode | One of the following modes at which the lock is granted: EX, CW, CR, PW, PR, NL. |
| RQ Mode | One of the following modes at which the lock is requested: EX, CW, CR, PW, PR, NL. |
| Duration | The length of time the lock has been in the current queue (since the console application found the lock). |
| Flags | The flags specified with the $ENQ(W) request. |
You can open a window about a specific process in the Single Lock Summary window by double-clicking on the process name.
Processes that are labeled unknown are associated with system locks. They cannot be opened. |
DECamds detects the following single lock-related events and displays them in the Event Log window. Node is replaced by the name of the node to which the event is related. Process is replaced by the name of the process to which the event is related.
LCKBLK, node process blocking resource resource
LCKWAT, node process waiting for resource resource granted to process on node node
The Cluster Transition/Overview Summary window shown in Figure 3-15 displays information about each node in an OpenVMS Cluster. This window is very similar to the System Overview window; however, the Cluster Transition window lists only one cluster for each set of nodes in a cluster, while the System Overview window lists all the nodes and the user-defined groups the nodes are in.
The window displays summary information as well as information about individual nodes: System Communication Services (SCS) name, SCS ID, Cluster System ID, Votes, Lock Directory Weight value, cluster status, and last transition time.
The data items shown in the window correspond to data that the Show Cluster utility displays for the SYSTEM and MEMBERS classes. A status field display of "unknown" usually indicates that DECamds is not communicating with the node.
Figure 3-15 Cluster Transition/Overview Summary Window
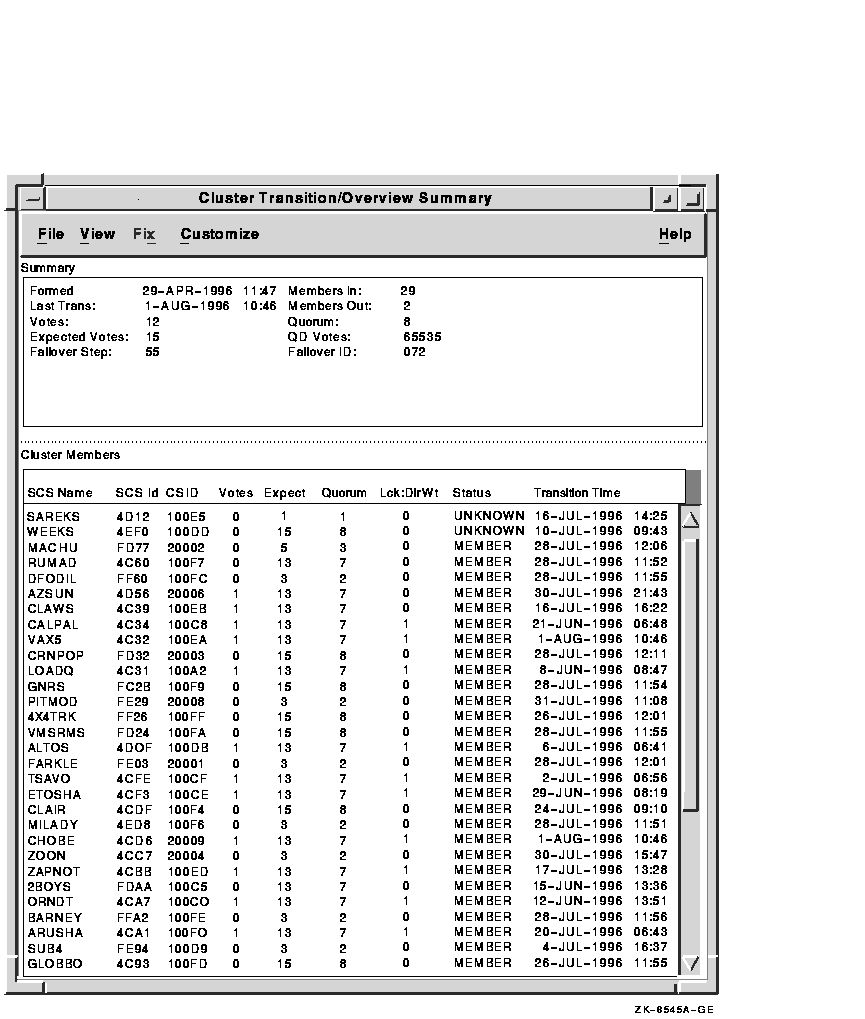
To open the Cluster Transition/Overview Summary window, do either of the following:
Note: The Cluster Transition Summary menu option is
not available for nodes that are not in the cluster; it is not
available from lines that display groups.
3.13.1 Data Displayed
The Cluster Transition/Overview window has two panel displays:
Table 3-14 describes the Summary panel data fields.
| Data Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Formed | Date and time the cluster was formed. |
| Last Trans | Date and time of the most recent cluster state transition. |
| Votes | Total number of quorum votes being contributed by all cluster members and quorum disk. |
| Expected Votes | Number of votes expected to be contributed by all members of the cluster as determined by the connection manager. This value is based on the maximum of the EXPECTED_VOTES system parameter and the maximized value of the VOTES system parameter. |
| Failover Step | Current failover step index; shows which step in the sequence of failover steps the failover is currently executing. |
| Members In | Number of members of the cluster DECamds has a connection to. |
| Members Out | Number of members of the cluster DECamds either has no connection to or has lost connection to. |
| Quorum | Number of votes required to keep cluster above quorum. |
| QD Votes | Number of votes given to Quorum Disk. A value of 65535 means there is no Quorum Disk. |
| Failover ID | Failover Instance Identification: unique ID of a failover sequence; indicates to system managers whether a failover has occurred since the last time they checked. |
Table 3-15 describes the Cluster Members panel data fields.
| Data Item | Description |
|---|---|
| SCS Name | System Communication Services name for the node (system parameter SCSNODE) |
| SCS id | System Communication Services identification for the node (system parameter SCSYSTEMID) |
| CSID | Cluster System Identification |
| Votes | Number of votes the member contributes |
| Expect | Expected votes to be contributed as set by the EXPECTED_VOTES system parameter |
| Quorum | Recommended quorum value derived from the expected votes |
| Lck:DirWt | Lock Manager distributed directory weight as determined by the LCKDIRWT system parameter |
| Status | Current cluster member status: MEMBER, UNKNOWN, or BRK_NON (break nonmember) |
| Transition Time | Time cluster member had last transition |
Following are notes about the display of data in the window:
LOVOTE, 'node' VOTES count is close to or below QUORUM
|
The System Communications Architecture Summary (SCA Summary) window shown in Figure 3-16 displays information about a selected node's virtual circuits and connections to other nodes in a cluster. (The display represents the view one node has of other nodes in the cluster.) More than one type of virtual circuit indicates that more than one path to the remote node exists.
Figure 3-16 SCA Summary Window
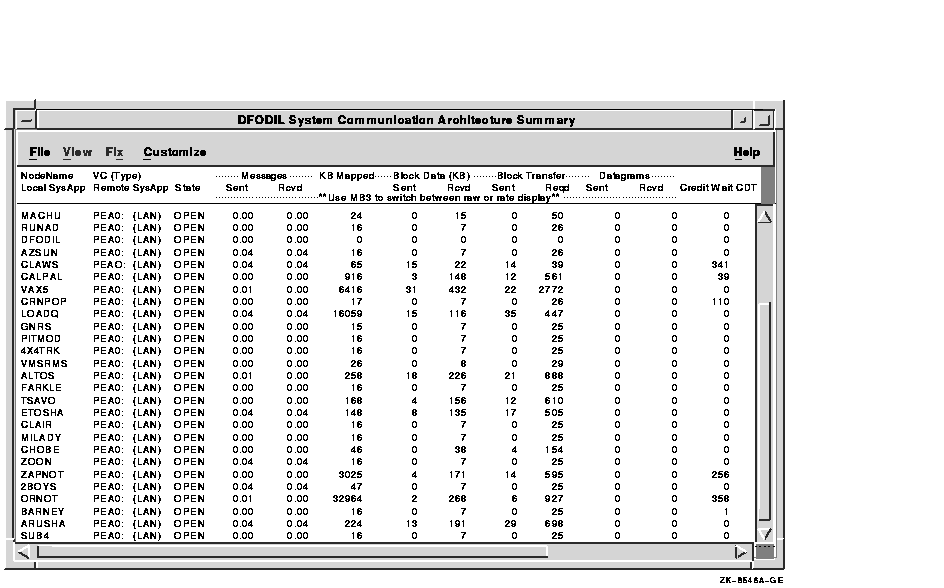
Each line in the window shows either a summary of all system applications (SysApps) using the virtual circuit communication or the communication on the connection between a local and a remote SysApp. The data displayed in the window is similar to the information that the Show Cluster utility displays for the CIRCUITS, CONNECTIONS, and COUNTERS classes. Unlike Show Cluster, however, this display shows only SCA connections to other OpenVMS nodes; it does not show SCA connections to the Disk Storage Architecture (DSA) or to devices such as FDDI or DSSI disk controllers.
By clicking MB3 on a node name and choosing View SysApps from the pop-up menu, you can display the system applications that are using virtual circuits. This option expands the list below a virtual circuit to show all the system applications that contribute to that virtual circuit. (The SysApp lines are dimmed and right-justified.)
To hide the display of system applications, click MB3 and choose Hide SysApps from the pop-up menu.
To display a menu that allows you to toggle between Raw and Rate data, click MB3 on the data to the right of the State field. (For messages, the default is the display of rate data; raw data is the default for all other types of data.)
To open an SCA Summary window, follow these steps:
Table 3-16 describes the SCA Summary window data fields.
| Data Item | Description |
|---|---|
| NodeName | SCS name of the remotely connected node. |
| VC(Type) | The virtual circuit being used and its type. |
| State | The state of the virtual circuit connection. |
| Messages | Relatively small data packets sent and received between nodes for control information. |
| Block Transfer | Fields listing the count of the number of block data transfers and requests initiated. |
| KB Mapped | Field listing the number of kilobytes mapped for block data transfer. Note: This field is available in Raw data format only. |
| Block Data (KB) | Fields listing in kilobytes the data transferred via block data transfer. |
| Datagrams | Number of unacknowledged messages sent between virtual circuits. |
| Credit Wait | Number of times the connection had to wait for a send credit. |
| CDT Wait | Number of times the connection had to wait for a buffer descriptor. |
| Local SysApp | Name of the local system application using the virtual circuit. |
| Remote SysApp | Name of the remote system application being communicated to. |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 5929PRO_004.HTML | ||