| Previous | Contents | Index |
A value of --1 indicates that the password could be marked as preexpired.
If you specify UAI$_PASSWORD2, the UAI$_PWD2_DATE item is ignored. To use these two item codes, you must use them in two separate calls. To generate a pre-expired password, follow the instructions in the the "Description" section at the end of this system service documentation. |
Because this decimal number is a byte in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 1 (byte).
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
By copying the item codes UAI$_SALT, UAI$_ENCRYPT, UAI$_PWD, UAI$_PWD_DATE, and UAI$_FLAGS, a site-security administrator can construct a utility that propagates password changes throughout the network. Note, however, that HP does not recommend using the same password on more than one node in a network.
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
To clear all the information in the user data area of the SYSUAF, specify $SETUAI with a buffer length field of 0.
Because the working set extent is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because the working set quota is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
The Set User Authorization Information service is used to modify the user authorization file (UAF) record for a specified user.The UAI$V_PWD_EXPIRED should only be set when the bit UAI$V_DISFORCE_PWD_CHANGE is set in the user's SYSUAF record and the comparison between the UAI$_PWD_DATE and UAI$_PWD_LIFETIME indicates a password is past its valid life.
To generate a pre-expired password, first generate a new hashed password using $HASH_PASSWORD. Then make a call to $SETUAI using either UAI$_PASSWORD or UAI$_PASSWORD2, as appropriate. Finally, make a separate call to $SETUAI to set UAI$_PWD_DATE or UAI$_PWD_DATE2 to -1.
For information about login and password expiration, see the Description section of the $GETUAI system service.
The following list describes the privileges you need to use the $SETUAI service:
- BYPASS or SYSPRV---Allows modification of any record in the UAF (user authorization file).
- GRPPRV---Allows modification of any record in the UAF whose UIC group matches that of the requester. Note, however, that you cannot change a UAF record whose UIC matches exactly the requester's UIC. Group managers with GRPPRV privilege are limited in the extent to which they can modify the UAF records of users in the same group; values such as privileges and quotas can be changed only if the modification does not exceed the values set in a group manager's UAF record.
- No privilege---Does not allow access to any UAF record.
None
$GETUAI
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The function code is invalid; the item list contains an invalid item code; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the reserved parameter has a nonzero value. SS$_NOGRPPRV The user does not have the privileges required to modify the authorization information for other members of the UIC group. SS$_NOSYSPRV The user does not have the privileges required to modify the authorization information associated with the user or for users outside of the user's UIC group. RMS$_RSZ The UAF record is smaller than required; the caller's SYSUAF is likely corrupt.
This service can also return OpenVMS RMS status codes associated with operations on indexed files. For a description of RMS status codes that are returned by this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
Performs initial setup for process preemption avoidance.
SYS$SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT enable
int sys$setup_avoid_preempt (int enable);
enable
OpenVMS usage: longword_unsigned type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Enables or disables preemption avoidance. If the enable argument is set to 1, preemption avoidance is enabled; if 0, preemption avoidance is disabled.
The Setup for Process Preemption Avoidance service is a kernel-mode initialization routine that locks the necessary internal data structures in memory so scheduling routines can access them above pageable IPL. A process or thread can then set or clear the indicator bit by calling the $AVOID_PREEMPT service.In addition, if the process or thread has ALTPRI privilege, $SETUP_AVOID_PREEMPT sets a bit in the PKTA (a per-kernel-thread data area) to mark that the process or thread can prevent preemption by other processes or threads having the same base priority but not those that have a higher base priority.
Note that without ALTPRI, this service will still function successfully, but will only enable the $AVOID_PREEMPT service to avoid preemptions due to quantum end.
None
None
$AVOID_PREEMPT
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully.
Also, any values returned by the $LKWSET or $UNLKSET services.
Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
SYS$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[new_tid] ,[old_tid]]
int sys$set_default_trans (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,...);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag that is set when the service completes. If this argument is omitted, event flag 0 is used.flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Flags specifying options for the service. The flags argument is a longword bit mask in which each bit corresponds to an option flag. The $DDTMDEF macro defines symbolic names for the option flag, described in Table SYS-54. All undefined bits must be 0. If this argument is omitted, no flags are used.
Table SYS-54 $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS Option Flag Flag Name Description DDTM$M_SYNC Specifies successful synchronous completion by returning SS$_SYNCH. When SS$_SYNCH is returned, the AST routine is not called, the event flag is not set, and the I/O status block is not filled in. iosb
OpenVMS usage: io_status_block type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
The I/O status block in which the completion status of the service is returned as a condition value. See the Condition Values Returned section.The following diagram shows the structure of the I/O status block:
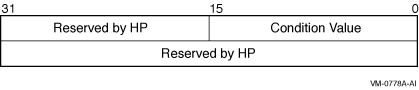
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | trans_id |
| type: | octaword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
A zero TID is returned if the calling process did not have a default transaction prior to the call.
The $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS system service:
- Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.
If either the new_tid argument passes the null value or the new_tid argument is omitted or zero, then the default transaction of the calling process is cleared. Otherwise the default transaction of the calling process is set to the value passed in the new_tid argument.- Returns the identifier (TID) of the previous default transaction of the calling process (the one that was set or cleared by this call to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS), if the old_tid argument is not zero.
$SET_DEFAULT_TRANS may fail for various reasons, including a call to $START_TRANS or $START_BRANCH that changes the default transaction of the calling process in progress.
Following a successful completion of $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS:
- The calling process does not have a default transaction, if either the new_tid argument passed the null value or the new_tid argument was omitted or zero.
- The default transaction of the calling process is that passed in the new_tid argument, if that argument was specified and its value was not zero.
- The identifier (TID) of the previous default transaction of the calling process is returned in the old_tid argument, if that argument was not omitted.
A null value is returned if the calling process did not previously have a default transaction.There is also a wait form of the service, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW.
None.
ASTLM
$ABORT_TRANS, $ABORT_TRANSW, $ACK_EVENT, $ADD_BRANCH, $ADD_BRANCHW, $CREATE_UID, $DECLARE_RM, $DECLARE_RMW, $END_BRANCH, $END_BRANCHW, $END_TRANS, $END_TRANSW, $FORGET_RM, $FORGET_RMW, $GETDTI, $GETDTIW, $GET_DEFAULT_TRANS, $JOIN_RM, $JOIN_RMW, $SETDTI, $SETDTIW, $SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW, $START_BRANCH, $START_BRANCHW, $START_TRANS, $START_TRANSW, $TRANS_EVENT, $TRANS_EVENTW
SS$_NORMAL If returned in R0, the request was successfully queued. If returned in the I/O status block, the service completed successfully. SS$_SYNCH The service completed successfully and synchronously (returned only if the DDTM$M_SYNC flag is set). SS$_ACCVIO An argument was not accessible to the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The options flags were invalid. SS$_EXASTLM The process AST limit (ASTLM) was exceeded. SS$_ILLEFC The event flag number was invalid. SS$_INSFARGS A required argument was missing. SS$_INSFMEM There was insufficient system dynamic memory for the operation. SS$_WRONGSTATE The default transaction was being changed at the time of the call.
Sets or clears the default transaction of the calling process.$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $SET_DEFAULT_TRANS.
SYS$SET_DEFAULT_TRANSW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb [,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,[new_tid] ,[old_tid]]
int sys$set_default_transw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb,...);
Modifies the characteristics of a device or the paths used to access that device.For synchronous completion, use the Set Device Characteristics and Wait ($SET_DEVICEW) service. The $SET_DEVICEW service is identical to the $SET_DEVICE service, except that $SET_DEVICEW returns to the caller only after the requested action has taken effect.
For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
SYS$SET_DEVICE [efn] [,chan] [,devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm] [,nullarg]
int sys$set_device (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void *devnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, struct_generic_64 *nullarg);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when $SET_DEVICE returns the requested information. The efn argument is a longword containing this number; however, $SET_DEVICE uses only the low-order byte.Upon request initiation, $SET_DEVICE clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when $SET_DEVICE returns the requested information, it sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
chan
OpenVMS usage: channel type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which information is desired. The chan argument is a word containing this number.To identify a device to $SET_DEVICE, you can specify either the chan or devnam parameters, but you should not specify both. If you specify both arguments, the chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor devnam, $SET_DEVICE uses a default value of 0 for chan.
devnam
OpenVMS usage: device_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor-fixed-length string descriptor
The name of the device about which $SET_DEVICE is to modify the characteristics or path settings. The devnam argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.The device name string can be either a physical device name or a logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore (_), the string is considered a physical device name; otherwise, the string is considered a logical name and logical name translation is performed until either a physical device name is found or the system default number of translations has been performed.
If the device name string contains a colon (:), the colon and the characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $SET_DEVICE, you can specify either the chan or devnam argument, but you should not specify both. If both arguments are specified, the chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor devnam, $SET_DEVICE uses a default value of 0 for chan.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.Currently, $SET_DEVICE allows only one valid item list entry.
The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
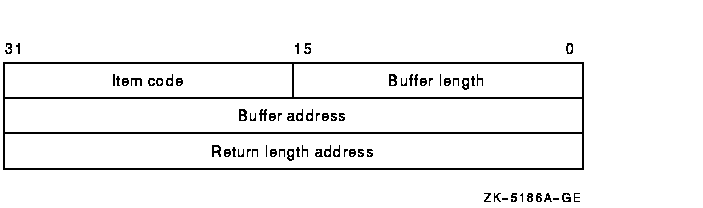
See the itmlst argument in the $GETDVI system service description for information on the meaning of these fields in the item list.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the caller of the $SET_DEVICE service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
SDV$_MP_SWITCH_PATH
Forces an immediate I/O path switch for the specified device. The active path will be switched from the current I/O path to the path name specified in the buffer for this item code. Note that issuing $SET_DEVICE with SDV$_MP_SWITCH_PATH will initiate the process of switching the path. A delay may occur between when the service completes and when the path switch is complete. A synchronous version of this service, $SET_DEVICEW, is available that will wait until the path switch attempt is complete before returning to the caller.The path name specified in this and the following item codes must be fully specified. It may be in either uppercase or lowercase, however the entire name must be specified.
The Return Length field in this and the following item codes should set to zero.
The SDVDEF macro contains these item codes.
SDV$_MP_DISABLE_PATH
Disables the path specified in the buffer for this item code so that it will no longer be considered as a switch candidate. Note that this does not apply to the current path, which cannot be disabled. The reasons one might want to disable a path include the following:
- You know a specific path is broken or that a failover to that path will cause some members of the cluster to lose access.
- To prevent automatic switching to a selected path while it is being serviced.
SDV$_MP_ENABLE_PATH
Re-enables the path name specified in the buffer for this item code as a switch candidate.
The Set Device service modifies the characteristics of devices or I/O paths that have been established to those devices. For Multipath, the service allows the user to switch the current I/O path to a different available path and to enable and disable paths from being used for I/O.None.
None.
$ASSIGN, $DASSGN, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DEVICE_PATH_SCAN, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The device name string descriptor, device name string, or itmlst argument cannot be read; or the buffer or return length longword cannot be written. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid item code, or the buffer length field in an item descriptor specified insufficient space for the return length information. SS$_DEVOFFLINE The specified path is not available. SS$_EXQUOTA Quota for pool has been exceeded. SS$_IVCHAN You specified an invalid channel number, that is, a channel number larger than the number of channels. SS$_IVDEVNAM The device name string contains invalid characters, or neither the devnam nor chan argument was specified. SS$_MPDEVBUSY The specified path for this device is temporarily unavailable. This condition is quite rare; if this status is returned, the operation should be retried immediately, because the cause of the unavailability is very short-lived. SS$_MPDEVUSERDISABLE The user has disabled the specified path for this device. SS$_NOOPER Caller does not have OPER privileges. SS$_NOPRIV The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more privileged access mode. SS$_NOSUCHDEV The specified device does not exist on the host system. SS$_NOSUCHPATH The specified pathname does not exist on the host system. SS$_PATHAMBIG The specified pathname is ambiguous for this device.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |