| Previous | Contents | Index |
Directs the output of an OpenVMS DECwindows application. Output can be directed from any processor running a DECwindows application, including workstations, to any DECwindows workstation.Both source and destination nodes must be part of the same network.
SET DISPLAY [display-device]
display-device
Specifies a logical name for the workstation display you are creating or modifying. If you are directing application output to multiple workstation displays, you can use different logical names to point to each display. If you do not specify a display-device parameter, the logical name DECW$DISPLAY is used. This means that, by default, application output will be displayed on the workstation display device referred to by DECW$DISPLAY.By entering the command SHOW DISPLAY, you can see the default workstation node where applications will be displayed, as well as related device, screen, and transport information.
If you specified your own logical name in the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command, include that logical name in the SHOW DISPLAY command.
DECwindows gives you the ability to run applications across a network. The SET DISPLAY command enables you to direct the output of client applications across the network to an alternate workstation (X display server) for viewing. For example, the SET DISPLAY command allows you to:
- Redirect the output from local client applications to a remote workstation for display.
- Redirect the output from remote client applications to your local workstation for display. Although the application runs on another processor, it looks the same as any other application running locally on your workstation.
By running applications on a remote processor for local display on your workstation monitor, you can take advantage of larger computers that might be better suited to a specific computing task. By default, applications running on your workstation are displayed on your workstation. While DECwindows must be available on both nodes, only the display (X server) node must be a workstation.
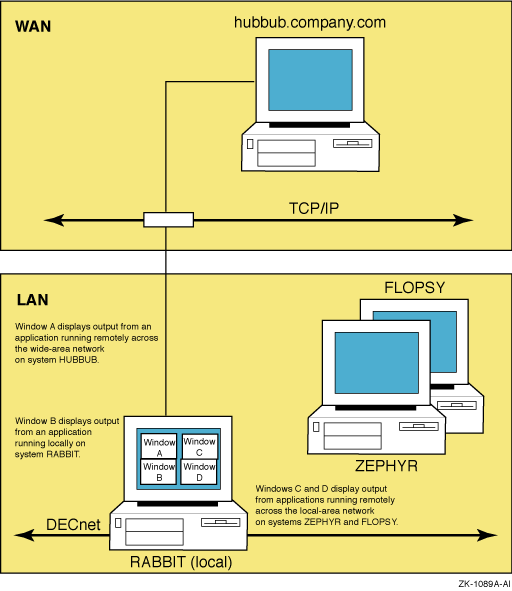
The SET DISPLAY command affects only those applications running from the process from which you enter the command. This means that although you might be running one application on your workstation and displaying it on another workstation, you can continue to run applications on your workstation for display in other windows on your workstation as illustrated in Figure DCLII-1.
Figure DCLII-1 Running Remote and Local Applications
Qualifiers to the SET DISPLAY command enable you to create the display device and manage aspects of the network connection between the client application and the X display server, as described in the following sections.
Redirecting Application or Display Output
To direct application output to another DECwindows workstation, enter the SET DISPLAY command in the following form:
|
SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=workstation_display/TRANSPORT=transport_name |
If you do not specify the /TRANSPORT qualifier, the value defined by the logical DECW$SETDISPLAY_DEFAULT_TRANSPORT is used. If this logical is not defined, the value of DECNET is used as the default.
Subsequently, you can redirect the display to other workstation devices by entering a DCL command in the following form:
|
SET DISPLAY/NODE=workstation_display |
By default, you are authorized to run client applications locally on your workstation (X display server). You cannot log into another node and direct applications to display on your workstation unless you explicitly authorize yourself to do so. This prevents unauthorized users on other nodes in the network from directing output to or receiving input from your workstation without your specific permission.
Using the DECwindows Session Manager, you or a privileged user can grant other users running remote applications access to your workstation using one of the following access control schemes:
Once access is granted, authorized users can use the SET DISPLAY command to create a display device that accesses the remote workstation, or more specifically, the remote X display server.
When using a display device to access a remote X display server, make sure that the node or host name you specify in the SET DISPLAY command represents a workstation on which you are authorized to display applications. For example, if you specify SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=HUBBUB from node ZEPHYR, and are not authorized to display applications on the workstation HUBBUB, an error message is displayed indicating that you are not authorized to use the device.
On Alpha and I64 systems, the /GENERATE, /REVOKE, and /[NO]XAUTHORITY qualifiers to SET DISPLAY enable you to specify additional authorization information when directing client applications to a workstation that uses a token-based access control scheme.
The MIT-KERBEROS-5 protocol does not currently support key generation, as defined by the SECURITY extension. Do not use the /GENERATE and /REVOKE qualifiers when connecting to an X display server protected by Kerberos access control. |
For information about displaying applications on other workstation nodes, using the DECwindows Session Manager to authorize remote connections, and supported access control schemes see the DECwindows documentation.
Using Proxy Servers (Alpha/I64 Only)
Some system configurations use Low-Bandwidth X (LBX) proxy servers to manage communication between client applications and one or more X display servers. With DECwindows, an LBX proxy server configuration can be categorized as either standalone or managed. Managed configurations use a proxy manager application to further filter and direct incoming connection requests by client applications.
The /PROXY qualifier specifies that a proxy manager application be used to locate a managed proxy server. The /PMPORT and /PMTRANSPORT qualifiers identify the port and network transport for the proxy manager. The /[NO]LBXAUTHENTICATE and /LBXDATA qualifiers specify the authorization protocol used between the proxy server and the X display server.
For information about using and configuring an LBX proxy server or a proxy manager, see the DECwindows documentation.
Specifying Named Properties (Alpha/I64 Only)
Named property values are designed to store configuration information associated with the display device, such as the network address of a session manager. By using the /VALUE qualifier, you can set or modify one or more values associated with the display device.
See also the description of the SHOW DISPLAY command for more information.
By using one of the following qualifiers: /EXECUTIVE_MODE, /SUPERVISOR_MODE, or /USER_MODE, you can specify the mode of the device you are creating. The default is the /SUPERVISOR_MODE qualifier.
See also the description of the SHOW DISPLAY command for more information.
/CREATE
Creates the workstation display device (WSAn:) on which a DECwindows application is displayed. You must specify the /CREATE qualifier the first time you use the SET DISPLAY command, but you need not respecify it if you continue to redirect output from applications to other workstations with subsequent SET DISPLAY commands.When you specify the /CREATE qualifier without the /NODE qualifier, the workstation device defaults to the current node. Additionally, if you omit the /TRANSPORT qualifier, the transport defaults to either the value specified by the DECW$SETDISPLAY_DEFAULT_TRANSPORT logical, if defined, or to DECNET.
/DELETE
Cancels the redirected display by deassigning the logical name DECW$DISPLAY and deleting the created display device. If you specified a logical name as the display-device parameter with the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command, entering the SET DISPLAY/DELETE display-device command cancels the redirected display by deassigning the logical name you specified and deleting the created display device.The DECwindows Session Manager defines DECW$DISPLAY in your job logical name table when you open a terminal (DECterm) window. When you redirect application output to another workstation with the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command, an additional DECW$DISPLAY logical name is defined in your process logical name table. This definition supersedes the definition in the job logical name table. Output from applications run from the process in which you executed the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command will be displayed on the workstation referred to by the definition of DECW$DISPLAY in the process logical name table. Enter the SHOW DISPLAY command to see where this application will be displayed. To see whether multiple definitions for DECW$DISPLAY exist, enter the command SHOW LOGICAL DECW$DISPLAY.
If DECW$DISPLAY is still defined (for example, in the job logical name table) after you specify the /DELETE qualifier, any DECwindows applications run from this process will be displayed on the workstation device to which output is now directed. Enter the SHOW DISPLAY command if you are unsure of the node to which DECW$DISPLAY refers.
Caution
If you modify or delete the definition of DECW$DISPLAY from the job logical name table, you will be unable to start another session. Be careful not to specify the /DELETE qualifier without having first redirected the display with the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command.You cannot specify the /DELETE and /CREATE qualifiers on the same command line.
/EXECUTIVE_MODE
Creates an executive-mode device and assigns the logical name DECW$DISPLAY to point to it. This qualifier must be used with the /CREATE qualifier. Devices created with the /EXECUTIVE_MODE qualifier are deleted only in the following situations:
- They are explicitly deleted with the /DELETE qualifier.
- The system is rebooted.
To modify or delete executive-mode devices, you must have SYSNAM (system logical name) privilege.
/GENERATE[=(keyword[=value][,...]) (Alpha/I64 only)
Requires a trusted network connection to an X display server and the SECURITY extension must be enabled on that server.Instructs the display device to connect to the X display server and generate a new authorization key (consisting of the authorization protocol name and a magic cookie). This authorization key is then stored in the X authority file currently in use. If you do not want to overwrite any previously existing keys for this display device, use the /XAUTHORITY qualifier to write the generated key to an alternate X authority file.
Note
The MIT-KERBEROS-5 protocol does not currently support key generation, as defined by the SECURITY extension. Do not use the /GENERATE qualifier when connected to an X display server protected by Kerberos access control.Each generated key follows the default settings unless otherwise specified. This means that, by default, each generated authorization key:
- Follows the MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1 protocol
- Grants an untrusted connection to the X server
- Is not associated with a particular application group
- Maintains a timeout period of 60 seconds before which it must be used (otherwise, it is automatically revoked)
Possible keyword values are as follows:
Value Description TRUSTED Specifies that the key grant unrestricted access to the X server. This keyword permits a client application to perform all actions. UNTRUSTED Specifies that the key grant restricted access to the X server. This keyword restricts client applications to a subset of X server extensions and prevents access to windows other than those created by the requesting application. TIMEOUT=seconds Specifies the number of seconds after which the key is revoked automatically if not in use. The timeout period begins immediately, and refreshes once all connections using this key have closed. NOTIMEOUT Specifies that the key has no expiration and must be explicitly revoked. GROUP=groupid Specifies that the key is associated with a particular application group and is to be revoked if that group is deleted. Although the use of application groups is supported by DECwindows Motif via the XC-APPGROUP extension, DECwindows Motif does not currently supply any utilities or desktop applications to create these groups. To create an application group, you must use an X Window System application or utility external to DECwindows Motif. PROTOCOL=name Specifies the protocol to be used to authenticate the key. Valid values are server dependent. For the DECwindows X display server, the only valid value for the name parameter is MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1. If you are connecting to a third-party X server, the names of any additional authorization protocols on that X server that support the SECURITY extension and key generation are also valid. The keyword sets TRUSTED/UNTRUSTED and TIMEOUT/NOTIMEOUT are mutually exclusive. Do not enter both values on the same command line.
/LBXAUTHENTICATE=protocol-name (Alpha/I64 only)
/NOLBXAUTHENTICATE (Alpha/I64 only)
Specifies the authorization protocol used to grant the LBX proxy server access to the X display server. This qualifier is used with the /PROXY and /CREATE qualifiers when creating an initial LBX proxy server connection. If a proxy server connection already exists, these qualifiers are ignored. If you do not specify /LBXAUTHENTICATE, the authorization protocol is obtained from the current X authority file. If you specify /NOLBXAUTHENTICATE, the proxy server defaults to the X authority file of the user who started the proxy manager application.Valid values for the protocol-name parameter are MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1 and MIT-KERBEROS-5. If you supply a protocol-name value of MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1, you must also specify the value of the magic cookie using the /LBXDATA qualifier.
/LBXDATA=value (Alpha/I64 only)
Specifies a data value for the authorization protocol used between the LBX proxy server and the X display server. This qualifier must be used with the /LBXAUTHENTICATE, /PROXY, and /CREATE qualifiers.When you issue a SET DISPLAY/CREATE/PROXY/LBXAUTHENTICATE=MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1 command, use this qualifier to provide a hexadecimal magic cookie value to the MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1 protocol.
/NODE=workstation_display
Defines the workstation on which you want to display DECwindows applications. The node name you provide cannot be a cluster alias (a name that represents multiple nodes configured in an OpenVMS Cluster), but must instead identify an actual node.You must create a workstation display device with the /CREATE qualifier before you can redirect the output from applications to other workstations. Do not enter the SET DISPLAY/NODE=workstation_display command without having previously specified the /CREATE qualifier.
When you specify the /CREATE qualifier without the /NODE qualifier, the workstation defaults to the current node.
Make sure that you are authorized to display applications on the workstation you specify. For more information about using the DECwindows Session Manager to authorize yourself to display applications from other nodes, see the DECwindows documentation.
Each node, both source and destination, must be defined in the other's network node database. For example, to display applications on node HUBBUB from ZEPHYR, HUBBUB must be entered in ZEPHYR's network node database, and ZEPHYR must be entered in HUBBUB's network node database. In addition, users on ZEPHYR must be authorized in the DECwindows Session Manager to display applications on HUBBUB. For information about entering nodes in a network node database, see the DECnet-Plus for OpenVMS documentation.
/PMPORT=[port-number] (Alpha/I64 only)
Specifies the port number on which the proxy manager is listening. This qualifier is used with the /PROXY and /CREATE qualifiers. The default port is 6500./PMTRANSPORT=transport-name (Alpha/I64 only)
Specifies the network transport used to connect to the proxy manager. This qualifier is used with the /PROXY and /CREATE qualifiers.Valid values for the transport-name parameter are the same as those listed for the /TRANSPORT qualifier. If you do not specify a transport, then the network transport specified by the /TRANSPORT qualifier is used.
/PROXY[=node] (Alpha/I64 only)
Specifies that a proxy manager application should be used to locate an LBX proxy server, which serves as an intermediary for processing client and server connections for a display device. Use an LBX proxy server when connecting to a remote node located over a low-bandwidth network connection, such as the Internet. The proxy manager should run on the local network. This qualifier is used with the /CREATE qualifier.When you create a display device using the SET DISPLAY/CREATE/PROXY command, you can use that device to connect to an X display server exactly the same as you would with any other display device. The client connects to the LBX proxy server returned by the proxy manager, which in turn connects to the X display server.
The value of the /PROXY qualifier specifies the node on which the proxy manager is running. The proxy manager is responsible for starting or locating a proxy server to provide access to the X display server specified by the transport, node, and server values. The proxy manager returns the transport, node, and server values for the selected proxy server to the display device. If you do not specify a value for the node parameter, the default location is the current node.
The /PMPORT and /PMTRANSPORT qualifiers can be used to further specify the proxy manager's location.
/QUOTA=(quota-name=value[,...]) (Alpha/I64 only)
Requires SYSPRV (system privilege) privilege or the DECW$WS_QUOTA rights identifier. If using an executive mode device, SYSNAM (system name) privilege is also required.Modifies the value of the name count or data space quota associated with the display device. These quotas influence the amount of non-paged pool available for storing named properties.
Possible values for the quota-name parameter are as follows:
- NAME_COUNT -- The name count quota restricts the total number of named properties associated with the device. The default name count quota is the value of the DECW$WS_DEFAULT_NAME_COUNT logical, or 12 if the logical is not defined.
- DATA_SPACE -- The data space quota restricts the total amount of space available (in bytes) for storing property values. Note that this space includes some data overhead and may not total the exact length of the values. The default data space quota is the value of the DECW$WS_DEFAULT_DATA_SPACE logical, or 10752 if the logical is not defined.
/REVOKE (Alpha/I64 only)
Requires a trusted network connection to an X display server and that the SECURITY extension be enabled on that server.Revokes an authorization key created with the /GENERATE qualifier.
If you specify the /REVOKE qualifier, the revoke operation is performed before the other actions on the SET DISPLAY command. For example, you can use both the /REVOKE and /GENERATE qualifiers on the same command line, in any order, to revoke one key and generate another.
Do not use with the /CREATE qualifier.
/SCREEN=screen-number
Defines the screen to be associated with this display device. In some hardware configurations, the system supports more than one screen. In such a configuration, you can specify the screen to which the application is directed./SERVER=server-number
Defines the server to be associated with the display device indicated by the display-device parameter to the SET DEVICE command. Using the transport mechanism, the server passes data between the user and the application. In some hardware configurations, the system supports more than one server. In such a configuration, you can specify the server to which the application is directed.On Alpha and I64 systems in LBX proxy server configurations, this qualifier specifies either an X display server or a standalone LBX proxy server. Standalone LBX proxy servers are not managed by the proxy manager and are manually assigned a server number on startup.
If you do not specify the display-device parameter, the SET DISPLAY/SERVER command associates the server with the display device indicated by the logical name DECW$DISPLAY.
/SUPERVISOR_MODE (default)
Creates a supervisor-mode device and assigns the logical name DECW$DISPLAY to point to it. This qualifier must be used with the /CREATE qualifier. When the user logs out, the device is deleted./TRANSPORT=transport-name
Defines the transport mechanism, for example, DECnet or local, that passes information between the application and the workstation. The transport mechanism is used to send input from the user to the application and output from the application to the display device. In proxy manager configurations, the value specified for this qualifier also acts as a default value for the /PMTRANSPORT qualifier.The transport-name parameter can be one of the following values:
- TCPIP or DECNET
Specifies the appropriate network transport for applications running and displaying on different nodes. You can specify the default transport value used with the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command by defining the DECW$SETDISPLAY_DEFAULT_TRANSPORT logical in the job, process, or system table. The value of this logical is then used each time you enter the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command without the /TRANSPORT qualifier. If you specify neither the qualifier nor the logical, the value of DECNET is used as default.- LOCAL
Optimizes the performance of applications running and displaying on the same node.On Alpha and I64 systems, the valid set of values for the transport-name parameter is further determined by the DECwindows logical DECW$IPV6_SUPPORT. This logical specifies which Internet Protocol version is supported: IPv4 or IPv6. See the DECwindows Motif documentation for more information about the DECW$IPV6_SUPPORT logical and support for the IPv6 protocol.
When using a proxy manager on Alpha and I64 systems, this qualifier specifies the transport that the selected LBX proxy server should use to connect to the X server.
When using a standalone proxy server (specified by the /SERVER qualifier), this qualifier specifies the transport that the client should use to connect to the proxy server.
/USER_MODE
Creates a user-mode display device and assigns the logical name DECW$DISPLAY to point to it. This qualifier must be used with the /CREATE qualifier. The lifetime of a user-mode device is one DECwindows image: when the next DECwindows image exits, the device is deleted./VALUE=(NAME=property-name,action[=data]) (Alpha/I64 only)
Sets, deletes, or modifies a named property value associated with the display device. Named property values are intended to store configuration information associated with the display device, such as the network address of a session manager.Use the following options to specify the type of action to perform:
- DELETE -- Deletes the specified property value.
- SET=data -- Sets the specified property to the supplied value.
- APPEND=data -- If the property exists, adds the supplied value to the end of list of values associated with the property. If the property does not exist, it is created and set to the supplied value.
Use the SHOW DISPLAY/VALUES command to display all existing named properties and their current values. Property names are restricted to 31 characters. Names that include a dollar sign ($) are reserved by HP for use with OpenVMS products and facilities. For example, names starting with the string DECW$ are reserved for DECwindows Motif.
/XAUTHORITY=[filespec] (Alpha/I64 only)
/NOXAUTHORITY (Alpha/I64 only)
Directs the display device to use a specific X authority file when connecting the X display server. The X authority file contains data that grants or restricts access to the X display server depending on the authorization protocol in use. If a file specification is not entered with this qualifier, the default of SYS$LOGIN:DECW$XAUTHORITY.DECW$XAUTH is used. If the file specification is entered and the file does not currently exist, it is created automatically when an entry is made into the file.Note that with this qualifier, all X authority file specifications resolve to a physical device (rather than a logical device) in order to remain available to other detached processes. If you specify a search list, and the file is not found, the X authority file specification resolves to the first directory in the search list.
Use /NOXAUTHORITY to clear the setting and return to the file referenced by the DECW$XAUTHORITY logical or the default file if the logical is not defined.
| #1 |
|---|
$ SHOW DISPLAY
Device: WSA1: [super]
Node: 0
Transport: LOCAL
Server: 0
Screen: 0
$ SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=ZEPHYR/EXECUTIVE_MODE
$ SHOW DISPLAY
Device: WSA2: [exec]
Node: ZEPHYR
Transport: DECNET
Server: 0
Screen: 0
$ SPAWN/NOWAIT/INPUT=NL: RUN SYS$SYSTEM:DECW$CLOCK
$ SET DISPLAY/DELETE
$ SHOW DISPLAY
Device: WSA1: [super]
Node: 0
Transport: LOCAL
Server: 0
Screen: 0
|
In this example, you are logged in to your workstation (device WSA1:), here referred to as node 0. (0 is the standard shorthand notation for representing your node.) You want to run the DECwindows Clock on your workstation and display it on another workstation, ZEPHYR.
Assuming you are authorized to display applications on ZEPHYR, you redirect the application's output to ZEPHYR with the SET DISPLAY command. The device created on ZEPHYR is an executive-mode device. You enter the SHOW DISPLAY command to verify the location of the redirected display. You then run Clock. When you finish running Clock, you disable the redirected display by entering the SET DISPLAY/DELETE command. Finally, you enter the SHOW DISPLAY command to verify that any applications subsequently run on your node will also be displayed there.
Note that a new workstation display device, WSA2, is created when you enter the SET DISPLAY/CREATE command. When you cancel the redirected display with the SET DISPLAY/DELETE command, application output is once again displayed on the workstation display device referred to by WSA1.
| #2 |
|---|
$ SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=FLOPSY RABBIT
$ SHOW DISPLAY RABBIT
Device: WSA2: [super]
Node: FLOPSY
Transport: DECNET
Server: 0
Screen: 0
$ RUN/DETACHED/OUTPUT=WSA2: SYS$SYSTEM:DECW$CLOCK
$ SET DISPLAY/CREATE/NODE=ZEPHYR ZNODE
$ SHOW DISPLAY ZNODE
Device: WSA3: [super]
Node: ZEPHYR
Transport: DECNET
Server: 0
Screen: 0
$ RUN/DETACHED/OUTPUT=WSA3: SYS$SYSTEM:DECW$CALENDAR
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:DECW$BOOKREADER
$ SHOW DISPLAY
Device: WSA1: [super]
Node: 0
Transport: LOCAL
Server: 0
Screen: 0
|
In this example, you are logged in to your node (device WSA1:), and want to direct the output from applications to several workstation displays in the same session. By specifying different logical names in the SET DISPLAY command, you can redirect the output without changing the logical name definition for DECW$DISPLAY. This allows you to display the output from most applications on your default display but occasionally display output on another workstation. You can also continue to run and display applications on your node. In this example, Clock is displayed on node FLOPSY, Calendar is displayed on node ZEPHYR, and Bookreader is displayed on your workstation.
Note that to run your applications with the DCL command RUN/DETACHED, you must use the device name that equates to the logical display device name you specified in the SET DISPLAY command. Use the SHOW DISPLAY command to obtain this device name.
| #3 |
|---|
$ SET DISPLAY/CREATE/GENERATE=TRUSTED-
_$ /XAUTHORITY=XAUTHORITY_TEMP/NODE=ZEPHYR
$ PIPE SHOW DISPLAY/EXTR | RSH FLOPSY "XAUTH NMERGE SYS$INPUT"
$ SET HOST FLOPSY
$ SET DISPLAY/NODE=ZEPHYR
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:DECW$CLOCK
|
In this example, you are logged into your workstation (WSA1:) and want to run the DECwindows Clock application on a remote node (FLOPSY) and display it on another workstation (ZEPHYR). Both systems are using Magic Cookie authorization to control access to the X display server.
Assuming you are already authorized to connect to the server on node ZEPHYR, you create a display device that connects to ZEPHYR and generates a new authorization key. This key grants trusted connections to the server on ZEPHYR within 60 seconds of key generation. To restrict trusted access to the server, the key is stored in a new X authority file, XAUTHORITY_TEMP.DECW$XAUTH.
The authorization key is then extracted and copied to FLOPSY, and merged with other entries in your X authority file on that system. You then set host to node FLOPSY and set display to node ZEPHYR. When you run the clock application from FLOPSY, it connects to the server on ZEPHYR and is allowed access as specified by the generated authorization key.
| #4 |
|---|
$ SET DISPLAY/CREATE/VALUE=-
_$ (NAME=DECW$SESSION_MANAGER,SET="tcpip/zephyr:9510")
$ SHOW DISPLAY/SYMBOLS/ALL
Device: WSA23: [super]
Node: 0
Transport: DECNET
Server: 0
Screen: 0
User-defined values:
"DECW$SESSION_MANAGER" = "tcpip/zephyr:9510"
$ SHOW SYMBOL DECW$DISPLAY__DECW$SESSION_MANAGER
DECW$DISPLAY__DECW$SESSION_MANAGER == "tcpip/zephyr:9510"
$ SET DISPLAY UNTRUSTED/CREATE/XAUTHORITY=TEMP/GENERATE-
_$ /VALUE=(NAME=DECW$SESSION_MANAGER,-)
_$ SET="'DECW$DISPLAY__DECW$SESSION_MANAGER'"
|
In this example, you create a display device, and set the DECW$SESSION_MANAGER property to the network address of a session manager on remote node ZEPHYR using port number 9510. The SHOW DISPLAY/SYMBOLS command then defines a DCL symbol for the port value. The symbol is then used to set the port value for a new display device.
| #5 |
|---|
$ SET DISPLAY/CREATE/PROXY=GATEWY/NODE=hubbub.company.com-
_$ /PMTRANSPORT=DECNET/NOLBXAUTHENTICATE/TRANSPORT=TCPIP
$ SHOW DISPLAY
Device: WSA23: [super]
Node: HUBBUB.COMPANY.COM
Transport: TCPIP
Server: 0
Screen: 0
Connection will use:
LBX proxy on node: gatewy.company.com
Transport to proxy: TCPIP
Server number: 63
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:DECW$CLOCK
|
In this example, you are logged into a local workstation (FLOPSY) and want to connect to an external host (hubbub.company.com), which is outside of your company's firewall. You use the proxy manager on a gateway host (GATEWY) to start the LBX proxy server, connect to the external host, and display the DECwindows Clock application.
Note that DECnet is used within the local area network (LAN) to communicate to the proxy manager, and TCP/IP is used by the proxy server to communicate to the X display server on the external host. When using a managed proxy server, the proxy server chooses the transport for the client-to-proxy server connection.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |