HP OpenVMS Version 8.3 New Features and
Documentation Overview
SDA$FID_TO_NAME
Translates a file identification (FID) into the equivalent file name.
Format
int sda$fid_to_name (char *devptr, unsigned short *fidptr, char
*bufptr, int buflen );
Arguments
devptr
| OpenVMS usage |
char_string |
| type |
character string |
| access |
read only |
| mechanism |
by reference |
The address of the device name string. The device name must be supplied
in allocation-class device name (ALLDEVNAM) format, but any leading
underscores or trailing colons are ignored.
fidptr
| OpenVMS usage |
address |
| type |
file identification |
| access |
read only |
| mechanism |
by reference |
The address of the three-word file identification.
bufptr
| OpenVMS usage |
char_string |
| type |
character string |
| access |
write only |
| mechanism |
by reference |
The address of a string buffer into which to store the file name string.
buflen
| OpenVMS usage |
longword |
| type |
longword (unsigned) |
| access |
read only |
| mechanism |
by value |
The maximum length of the string buffer.
Description
When analyzing the current system, this routine calls LIB$FID_TO_NAME
to translate the file identification into a file name. When analyzing a
dump, if there is a file data collection available and the specified
disk and file identification is included in the collection, the
recorded file name is returned. If there is no collection (for the
entire system, this disk, or just this file), this routine returns the
error condition SDA$_NOCOLLECT.
Condition Values Returned
|
SDA$_SUCCESS
|
File identification successfully translated.
|
|
SDA$_COLLECT
|
No collection available for the system, the specified disk, or the file
identification.
|
|
Others
|
An error occurred when LIB$FID_TO_NAME was called.
|
SDA$GET_FLAGS
Obtains environment flags that indicate how SDA is being used.
Format
int sda$get_flags (SDA_FLAGS *flagaddr);
Arguments
flagaddr
| OpenVMS usage |
address |
| type |
SDA_FLAGS structure |
| access |
write only |
| mechanism |
by reference |
The address of the location where the environment flags are to be
returned.
Description
SDA provides a set of flag bits that indicate whether it is being used
to analyze the current system, a system dump, a process dump, and so
on. The set of bits is defined in SDA_FLAGSDEF.H in
SYS$LIBRARY:SYS$LIB_C.TLB.
Condition Values Returned
3.16.3 ANALYZE Command Qualifier
The new SDA ANALYZE command /COLLECTION qualifier indicates to SDA that
the file ID translation data or unwind data can be found in a separate
file. If you specify this qualifier, it should follow the /CRASH_DUMP
qualifier in the command string. Use the following format:
/CRASH_DUMP/COLLECTION = collection-file-name
|
SDA can provide additional information when analyzing a dump if a
collection has been made of file identification translation data (on
both OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS for Integrity servers) and of unwind
data (on OpenVMS for Integrity servers only). This data is usually
saved when the dump file is copied using the SDA COPY/COLLECT command,
but it can be saved to a separate file using the COLLECT/SAVE command.
By default, COLLECT/SAVE creates a .COLLECT file with the same name and
in the same directory as the dump file. A subsequent ANALYZE/CRASH_DUMP
command uses this file automatically. If the collection file is in a
different location or if the collection previously appended to the dump
file is incomplete (for example, a disk was not mounted at the time of
the SDA COPY), the /COLLECTION qualifier can be used to specify an
alternate collection file.
At least one field of the collection file name must be specified, and
other fields default to the highest generation of the same file name
and location as the dump file, with a file type of .COLLECT.
3.16.4 DUMP Command Qualifiers
The SDA DUMP command has the following new qualifiers:
- /BYTE---Outputs each data item as a byte.
- /NOSUPPRESS---Indicates that SDA should not suppress leading zeroes
when displaying data in hexadecimal format.
- /WORD---Outputs each data item as a WORD.
3.16.5 SEARCH Command Qualifier
The SDA SEARCH command has the new /IGNORE_CASE qualifier, which
indicates to SDA that, when searching for a string, the case of any
alphabetic characters should be ignored. The default behavior is to
search for an exact match. This qualifier is ignored for value searches.
3.16.6 New SHOW CLUSTER Command Qualifier
The SDA SHOW CLUSTER command has the new /CIRCUIT=pb-addr
qualifier, which displays only the OpenVMS Cluster system information
for a specific path, where pb-addr is the address of its path
block. This qualifier is mutually exclusive with the
/ADDRESS=n, /CSID=csid, and /NODE=name
qualifiers. If you specify the /CIRCUIT=pb-addr qualifier, the
SHOW CLUSTER command displays only the information from the specified
path block.
3.16.7 SHOW CRASH Qualifier
The SDA SHOW CRASH command has the new /ALL qualifier, which displays
exception data for all CPUs. By default, the registers (on Alpha) or
exception frame contents (on Integrity servers) are omitted from the
display for any CPUs with CPUEXIT or DBGCPUEXIT bugchecks.
3.16.8 SHOW DUMP Command Qualifiers
The following new qualifiers have been added to the SHOW DUMP command:
- /COLLECTION[= { ALL|n }]
Displays the contents of the
file identification and/or unwind data collection appended to a copy of
the dump using COPY/COLLECT or written to a separate collection file
using COLLECT/SAVE. By default, a summary of the collection is
displayed. You can specify that the details of a single entry or all
entries are to be displayed. The n is the start block number
of the collection entry, as displayed in the collection summary.
- /FILE= { COLLECTION|DUMP }
If a separate collection file is in
use, the /FILE qualifier indicates to which file the SHOW DUMP command
applies. By default, SHOW DUMP/SUMMARY, SHOW DUMP/HEADER, SHOW
DUMP/COLLECTION and SHOW DUMP/ALL commands apply to both files. By
default, SHOW DUMP/BLOCK applies to the dump file. All other qualifiers
can apply only to the dump file.
3.16.9 SDA SHOW PROCESS Qualifier
The SDA SHOW PROCESS command has the new /CHECK qualifier, which checks
all free process pool packets for POOLCHECK-style corruption,in exactly
the same way that the system does when generating a POOLCHECK crash
dump.
3.16.10 Keywords Added to SHOW RESOURCES/STATUS Command
The following new keywords have been added to the SHOW RESOURCES/STATUS
qualifier:
- RM_FORCE---Forced tree move
- RM_FREEZE---Freeze resource tree on this node
- RM_INTEREST---Remaster due to master having no interest
- XVAL_VALID---Last value block was long block
3.16.11 SHOW UNWIND Qualifier
The SDA SHOW UNWIND command has the new qualifier,
/IMAGE=name, which displays the details of every unwind
descriptor for the specified system images (wildcards allowed).
3.17 System Parameters
A number of system parameters are introduced in OpenVMS Version 8.3.
The following table contains brief descriptions of these new
parameters. (More detailed descriptions of the parameters are in the
HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.)
| Parameter |
Description |
|
EXECSTACKPAGES
|
(Alpha and I64) EXECSTACKPAGES controls the number of pages allocated
for each RMS exec stack.
|
|
GB_CACHEALLMAX
|
(Alpha and I64) If a file is connected to RMS with the RMS global
buffer DEFAULT option enabled, the number of blocks cached is either a
maximum of the GB_CACHEALLMAX parameter or a percentage of the file,
whichever results in a larger global count.
|
|
GB_DEFPERCENT
|
(Alpha and I64) If a file is connected to RMS with the RMS global
buffer "DEFAULT" option enabled, either a percentage
(GB_DEFPERCENT) of the file is cached or up to GB_CACHEALLMAX blocks of
it are cached, whichever results in a larger global buffer count.
|
|
IO_PRCPU_BITMAP
|
(Alpha and I64) This parameter forms a bitmap representing up to 1024
CPUs. Bits set in this bitmap indicate CPUs that are available for use
as Fast Path preferred CPUs. IO_PRCPU_BITMAP defaults to all bits set.
(CPU 0 through CPU 1023 are all enabled for Fast Path port assignment.)
You may want to disable the primary CPU from serving as a preferred
CPU by leaving its bit clear in IO_PRCPU_BITMAP. This reserves the
primary CPU for non-Fast-Path IO operations to use.
|
|
LOCKRMWT
|
Can have a value from 0 to 10 and defaults to 5. Remaster decisions are
based on the difference in lock remaster weights between the master and
a remote node. LOCKRMWT is a dynamic parameter.
|
|
SCD_HARD_OFFLD
|
The scheduler hard off-load parameter is a CPU bitmask parameter. The
bits correspond to CPU IDs. For any bit set, the OpenVMS scheduler does
not schedule processes on this CPU unless the process has hard affinity
set for the CPU. The bit corresponding to the primary CPU is ignored.
SCH_HARD_OFFLD is a DYNAMIC parameter.
|
|
SCH_SOFT_OFFLD
|
The scheduler soft off-load parameter is a CPU bitmask parameter. The
bits correspond to CPU IDs. For any bit set, the OpenVMS scheduler
tries to avoid scheduling processes on this CPU. However, if no other
idle CPUs exist, processes are still scheduled on this CPU.
SCH_SOFT_OFFLD is a DYNAMIC parameter.
|
|
SCHED_FLAG
|
This special parameter is used by HP and is subject to change. Do not
change this parameter unless HP recommends that you do so.
|
|
SMP_CPU_BITMAP
|
(Alpha and I64) This parameter indicates that the corresponding CPU is
a bitmap representing up to 1024 CPUs. Each bit set in this bitmap
indicates that the corresponding CPU automatically attempts to join the
active set in an OpenVMS symmetric multiprocessing environment when the
instance is booted.
|
|
VCC_PAGESIZE
|
(Alpha and I64) VCC_PAGESIZE is a special parameter reserved for HP use
only. Extended File Cache intends to use this parameter in future
versions.
|
|
VCC_RSVD
|
(Alpha and I64) VCC_RSVD is a special parameter reserved for HP use
only. Extended File Cache intends to use this parameter in future
versions.
|
3.18 System Service Logging Enhancements
The system service logging (SSLOG) mechanism has been enhanced for
OpenVMS Version 8.3:
- When a system service request is logged, the CPU, kernel thread,
and POSIX threads IDs from which the service was requested are now
recorded.
The ANALYZE/SSLOG utility displays this new information
with other details from each entry.
You can selectively display
entries based on these characteristics through new /SELECT values:
| Value |
Description |
|
CPU
|
CPU ID
|
|
KTID
|
Kernel thread ID
|
|
TID
|
POSIX thread ID
|
- It is possible to have system service requests logged only to the
process's buffers and not to a file. This is, however, of very limited
use and not recommended, because accessing any of the information
logged would require finding the logging buffers in memory or in a
crashdump and formatting them manually.
You specify this type of
logging through a new value for the SET PROCESS/SSLOG qualifier FLAGS
value:
SET PROCESS/SSLOG=(STATE=ON[, FLAGS=[NO]FILE])
|
The default value for this flags is FILE.
- A process can be created with system service logging enabled. This
happens automatically when a process with logging enabled creates a
subprocess: logging characteristics of the parent are propagated to the
child.
Also, you can explicitly create a process with logging
enabled with a new $RUN command qualifier. The syntax for the RUN
command is
RUN /SSLOG_ENABLE=([COUNT=x][,SIZE=y]
[,FLAGS=([NO]ARG,[NO]FILE))]
|
Alternatively, you can request the $CREPRC system service with the
following new parameters:
- Flag PRC$M_SSLOG_ENABLE in argument stsflag, when
set, requests that system service logging be enabled in the new process.
- You can specify logging characteristics through item list entry
types PRC$C_SSLOG_FLAGS, PRC$C_SSLOG_BUFSIZE, and PRC$C_SSLOG_BUFCNT.
Regardless of how the process is created, logging does not begin
until after the process's first image has been fully activated.
System service logging is described in detail in the HP OpenVMS System Analysis Tools Manual.
3.19 SYS$ACM-Enabled LOGINOUT.EXE and SETP0.EXE Images for LDAP Authentication
Important
The images described in this section are "pre-production"
images and are not qualified for production use. Once additional
rigorous "production-quality" testing and qualification is
completed, a maintenance update (ECO) will be made available to allow
for production use deployments of the SYS$ACM-enabled
loginout and setp0 images.
|
This release provides optional LOGINOUT.EXE and SETP0.EXE (SET
PASSWORD) images that use the SYS$ACM system service for user
authentication and password changes.
When these images are used, login and password change requests are sent
to the SYS$ACM service and handled by the ACME_SERVER process's
authentication agents.
A VMS authentication agent is configured by default to service standard
VMS login and password-change requests. In addition, you can install an
LDAP authentication agent that services login and password-change
requests using an LDAP version 3 directory server.
For more information, see the SYS$HELP:ACME_DEV_README.TXT file.
3.20 Time Zones Added
OpenVMS Version 8.3 provides 544 time zones based on the time-zone
public database named tzdata2006b. Five new time zones have been added
in OpenVMS Version 8.3:
Australia/Currie
America/Coral_Harbour
America/Indiana/Vincennes
America/Indiana/Petersburg
America/Moncton
An additional 12 time zones were added in Version 8.2--1 but were not
documented:
America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires
America/Argentina/Catamarca
America/Argentina/Comodrivadavia
America/Argentina/Cordoba
America/Argentina/Jujuy
America/Argentina/La_Rioja
America/Argentina/Mendoza
America/Argentina/Rio_Gallegos
America/Argentina/San_Juan
America/Argentina/Tucuman
America/Argentina/Ushuaia
Europe/Mariehamn
These new time zones will be added to an appendix in the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual
the next time it is updated.
The following time zones have been deleted:
- SystemV/AST4ADT
- SystemV/EST5EDT
- SystemV/CST6CDT
- SystemV/MST7MDT
- SystemV/PST8PDT
- SystemV/YST9YDT
- SystemV/AST4
- SystemV/EST5
- SystemV/CST6
- SystemV/MST7
- SystemV/PST8
- SystemV/YST9
- SystemV/HST10
Note
With the passage of the Energy Policy Act in 2005 in the United States,
starting in March 2007; daylight saving time (DST) will begin on the
second Sunday in March (instead of the current first Sunday in April).
DST will end on the first Sunday in November (instead of the current
last Sunday in October). The latest time-zone rules have been
incorporated into OpenVMS Version 8.3.
Patch kits for OpenVMS Versions 7.3--2, 8.2, and 8.2--1 are provided on
the OpenVMS Alpha Version 8.3 Operating System CD and the OpenVMS for
Integrity servers Version 8.3 DVD.
|
3.21 Virtual LAN (VLAN) Support in OpenVMS
Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a mechanism for segmenting a LAN broadcast domain
into smaller sections. The IEEE 802.1Q specification defines the
operation and behavior of a VLAN. The OpenVMS implementation adds IEEE
802.1Q support to selected OpenVMS LAN drivers so that OpenVMS can now
route VLAN tagged packets to LAN applications using a single LAN
adapter.
You can use VLAN to do the following:
- Segment specific LAN traffic on a network for the purposes of
network security or traffic containment, or both.
- Use VLAN isolated networks to simplify address management
VLAN Design
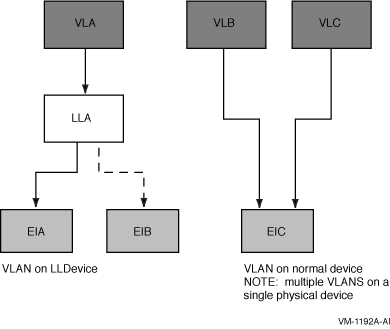
In OpenVMS, VLAN presents a virtual LAN device to LAN applications. The
virtual LAN device associates a single IEE 802.1Q tag with
communications over a physical LAN device. The virtual device provides
the ability to run any LAN application (for example, SCA, DECnet,
TCP/IP, or LAT) over a physical LAN device, allowing host-to-host
communications as shown in Figure 3-1.
Note
DECnet-Plus and DECnet Phase IV can be configured to run over a VLAN
device.
|
Figure 3-1 Virtual LAN
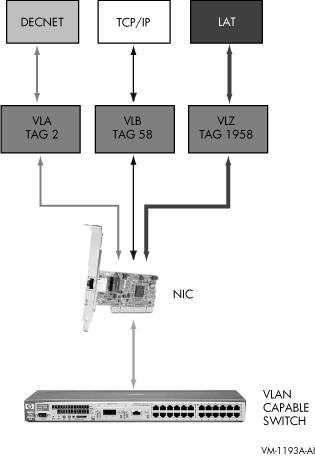
OpenVMS VLAN has been implemented through a new driver,
SYS$VLANDRIVER.EXE, which provides the virtual LAN devices. Also,
existing LAN drivers have been updated to handle VLAN tags. LANCP.EXE
and LANACP.EXE have been updated with the ability to create and
deactivate VLAN devices and to display status and configuration
information.
The OpenVMS VLAN subsystem was designed with particular attention to
performance. Thus, the performance cost of using VLAN support is
negligible.
When configuring VLAN devices, keep in mind that VLAN devices share the
same locking mechanism as the physical LAN device. For example, running
OpenVMS cluster protocol on a VLAN device along with the underlying
physical LAN device does not result in increased benefit and might, in
fact, hinder performance.
3.21.1 VLAN Support Details
All supported Gigabit and 10-Gb (I64-only) LAN devices are capable of
handling VLAN traffic on Alpha and I64 systems.
The following list describes additional details of VLAN-related support: