 |
HP OpenVMS systems documentation |
| Previous | Contents | Index |
There is an OpenVMS name for each Fibre Channel storage adapter, for
each path from the storage adapter to the storage subsystem, and for
each storage device. These sections apply to both disk devices and tape
devices, except for Section 7.4.2.3, which is specific to disk devices.
Tape device names are described in Section 7.5.
7.4.2.1 Fibre Channel Storage Adapter Names
Fibre Channel storage adapter names, which are automatically assigned by OpenVMS, take the form FGx0 :
The naming design places a limit of 26 adapters per system. This naming may be modified in future releases to support a larger number of adapters.
Fibre Channel adapters can run multiple protocols, such as SCSI and LAN. Each protocol is a pseudodevice associated with the adapter. For the initial implementation, just the SCSI protocol is supported. The SCSI pseudodevice name is PGx0 , where x represents the same unit letter as the associated FGx0 adapter.
These names are illustrated in Figure 7-13.
Figure 7-13 Fibre Channel Initiator and Target Names
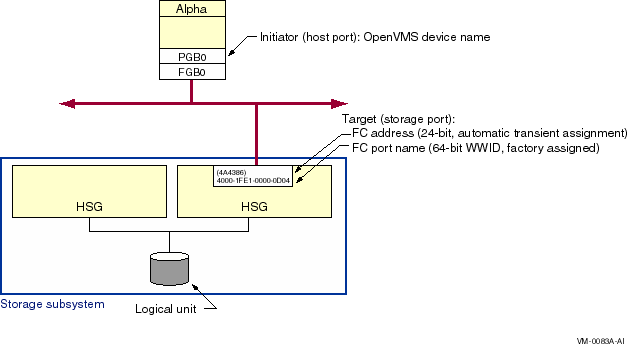
With the introduction of multipath SCSI support, as described in Chapter 6, it is necessary to identify specific paths from the host to the storage subsystem. This is done by concatenating the SCSI pseudodevice name, a decimal point (.), and the WWID of the storage subsystem port that is being accessed. For example, the Fibre Channel path shown in Figure 7-13 is named PGB0.4000-1FE1-0000-0D04.
Refer to Chapter 6 for more information on the display and use of
the Fibre Channel path name.
7.4.2.3 Fibre Channel Disk Device Identification
The four identifiers associated with each FC disk device are shown in Figure 7-14.
Figure 7-14 Fibre Channel Disk Device Naming
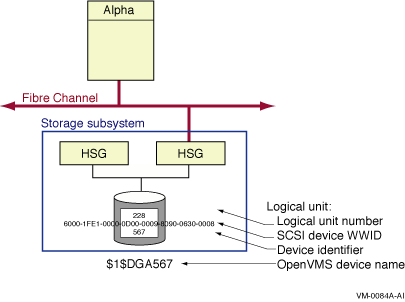
The logical unit number (LUN) is used by the system as the address of a specific device within the storage subsystem. This number is set and displayed from the HSG or HSV console by the system manager. It can also be displayed by the OpenVMS SDA utility.
Each Fibre Channel disk device also has a WWID to provide permanent, unique identification of the device. The HSG or HSV device WWID is 128 bits. Half of this identifier is the WWID of the HSG or HSV that created the logical storage device, and the other half is specific to the logical device. The device WWID is displayed by the SHOW DEVICE/FULL command, the HSG or HSV console and the AlphaServer console.
The third identifier associated with the storage device is a user-assigned device identifier. A device identifier has the following attributes:
The device identifier has a value of 567 in Figure 7-14. This value is used by OpenVMS to form the device name so it must be unique throughout the cluster. (It may be convenient to set the device identifier to the same value as the logical unit number (LUN). This is permitted as long as the device identifier is unique throughout the cluster.)
A Fibre Channel storage disk device name is formed by the operating system from the constant $1$DGA and a device identifier, nnnnn. Note that Fibre Channel disk device names use an allocation class value of 1 whereas Fibre Channel tape device names use an allocation class value of 2, as described in Section 7.5.2.1. The only variable part of the name is its device identifier, which you assign at the HSG or HSV console. Figure 7-14 shows a storage device that is known to the host as $1$DGA567.
A device identifier of 0 is not supported on the HSV. |
The following example shows the output of the SHOW DEVICE/FULL display for this device:
$ SHOW DEVICE/FULL $1$DGA567:
Disk $1$DGA567: (WILD8), device type HSG80, is online, mounted, file-oriented
device, shareable, device has multiple I/O paths, served to cluster via MSCP
Server, error logging is enabled.
Error count 14 Operations completed 6896599
Owner process "" Owner UIC [SYSTEM]
Owner process ID 00000000 Dev Prot S:RWPL,O:RWPL,G:R,W
Reference count 9 Default buffer size 512
WWID 01000010:6000-1FE1-0000-0D00-0009-8090-0630-0008
Total blocks 17769177 Sectors per track 169
Total cylinders 5258 Tracks per cylinder 20
Host name "WILD8" Host type, avail Compaq AlphaServer GS160 6/731, yes
Alternate host name "H2OFRD" Alt. type, avail AlphaServer 1200 5/533 4MB, yes
Allocation class 1
Volume label "S5SH_V72_SSS" Relative volume number 0
Cluster size 18 Transaction count 9
Free blocks 12811860 Maximum files allowed 467609
Extend quantity 5 Mount count 6
Mount status System Cache name "_$1$DGA8:XQPCACHE"
Extent cache size 64 Maximum blocks in extent cache 1281186
File ID cache size 64 Blocks currently in extent cache1260738
Quota cache size 0 Maximum buffers in FCP cache 1594
Volume owner UIC [1,1] Vol Prot S:RWCD,O:RWCD,G:RWCD,W:RWCD
Volume Status: ODS-2, subject to mount verification, file high-water marking,
write-back caching enabled.
Volume is also mounted on H2OFRD, FIBRE3, NORLMN, BOOLA, FLAM10.
I/O paths to device 5
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D02 (WILD8), primary path.
Error count 0 Operations completed 14498
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D03 (WILD8), current path.
Error count 14 Operations completed 6532610
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D01 (WILD8).
Error count 0 Operations completed 14481
Path PGA0.5000-1FE1-0000-0D04 (WILD8).
Error count 0 Operations completed 14481
Path MSCP (H2OFRD).
Error count 0 Operations completed 320530
|
This section describes the configuration requirements and user commands
necessary to utilize the Fibre Channel tape functionality. Fibre
Channel tape functionality refers to the support of SCSI tapes and SCSI
tape libraries in an OpenVMS Cluster system with shared Fibre Channel
storage. The SCSI tapes and libraries are connected to the Fibre
Channel by a Fibre-to-SCSI bridge. Currently, two bridges are
available: the Modular Data Router (MDR) and the Network Storage Router
(NSR).
7.5.1 Minimum Hardware Configuration
Following is the minimum Fibre Channel tape hardware configuration:
Tapes are not supported in an HSGxx storage subsystem nor behind a Fibre Channel Tape Controller II (FCTC-II). A tape library robot is an example of a medium changer device, the term that is used throughout this section. |
This section provides detailed background information about Fibre Channel Tape device naming.
Tape and medium changer devices are automatically named and configured
using the SYSMAN IO FIND and IO AUTOCONFIGURE commands described in
Section 7.5.3. System managers who configure tapes on Fibre Channel
should refer directly to this section for the tape configuration
procedure.
7.5.2.1 Tape and Medium Changer Device Names
Fibre Channel tapes and medium changers are named using a scheme similar to Fibre Channel disk naming.
On parallel SCSI, the device name of a directly attached tape implies the physical location of the device; for example, MKB301 resides on bus B, SCSI target ID 3, and LUN 1. Such a naming scheme does not scale well for Fibre Channel configurations, in which the number of targets or nodes can be very large.
Fibre Channel tape names are in the form $2$MGAn. The letter for the controller is always A, and the prefix is $2$. The device mnemonic is MG for tapes and GG for medium changers. The device unit n is automatically generated by OpenVMS.
The name creation algorithm chooses the first free unit number, starting with zero. The first tape discovered on the Fibre Channel is named $2$MGA0, the next is named $2$MGA1, and so forth. Similarly, the first medium changer detected on the Fibre Channel is named $2$GGA0. The naming of tapes and medium changers on parallel SCSI buses remains the same.
Note the use of allocation class 2. Allocation class 1 is already used by devices whose name is keyed by a user-defined identifier (UDID), as with HSG Fibre Channel disks ($1$DGAnnnn) and HSG console command LUNs ($1$GGAnnnn).
An allocation class of 2 is used by devices whose names are obtained from the file, SYS$DEVICES.DAT. The names are based on a worldwide identifier (WWID) key, as described in the following sections. Also note that, while GG is the same mnemonic used for both medium changers and HSG Command Console LUNs (CCLs), medium changers always have an allocation class of 2 and HSG CCLs an allocation class of 1.
Tape and medium changer names are automatically kept consistent within a single OpenVMS Cluster system. Once a tape device is named by any node in the cluster, all other nodes in the cluster automatically choose the same name for that device, even if this overrides the first free unit number algorithm. The chosen device name remains the same through all subsequent reboot operations in the cluster.
If multiple nonclustered Alpha systems exist on a SAN and need to
access the same tape device on the Fibre Channel, then the upper-level
application must provide consistent naming and synchronized access.
7.5.2.2 Use of Worldwide Identifiers (WWIDs)
For each Fibre Channel tape device name, OpenVMS must uniquely identify the physical device that is associated with that name.
In parallel SCSI, directly attached devices are uniquely identified by their physical path (port/target/LUN). Fibre Channel disks are uniquely identified by user-defined identifiers (UDIDs). These strategies are either unscalable or unavailable for Fibre Channel tapes and medium changers.
Therefore, the identifier for a given Fibre Channel tape or medium changer device is its worldwide identifier (WWID). The WWID resides in the device firmware and is required to be unique by the Fibre Channel standards.
WWIDs can take several forms, for example:
The overall WWID consists of the WWID data prefixed by a binary WWID header, which is a longword describing the length and type of WWID data.
In general, if a device reports an IEEE WWID, OpenVMS chooses this as the unique identifying WWID for the device. If the device does not report such a WWID, then the ASCII WWID is used. If the device reports neither an IEEE WWID nor serial number information, then OpenVMS does not configure the device. During the device discovery process, OpenVMS rejects the device with the following message:
%SYSMAN-E-NOWWID, error for device Product-ID, no valid WWID found. |
The WWID structures can be a mix of binary and ASCII data. These formats are displayable and are intended to be consistent with those defined by the console WWIDMGR utility. Refer to the Wwidmgr Users' Manual for additional information. (The Wwidmgr Users' Manual is available in the [.DOC] directory of the Alpha Systems Firmware Update CD-ROM.)
Note that if the data following the WWID header is pure ASCII data, it must be enclosed in double quotation marks.
The displayable format of a 64-bit IEEE WWID consists of an 8-digit hexadecimal number in ASCII (the WWID header), followed by a colon (:) and then the IEEE WWID data. For example:
0C000008:0800-4606-8010-CD3C |
The displayable format of an ASCII WWID consists of an 8-digit WWID header, followed by a colon (:) and then the concatenation of the 8-byte vendor ID plus the 16-byte product ID plus the serial number. For example:
04100022:"COMPAQ DLT8000 JF71209240" |
Occasionally, an ASCII WWID may contain nonprintable characters in the serial number. In a displayable format, such a character is represented by\nn, where nn is the 2-digit ASCII hexidecimal value of the character. For example, a null is represented by\00. |
Fibre Channel tape and medium changer devices are configured according to information found in the SYS$SYSTEM:SYS$DEVICES.DAT file. This is an ASCII file consisting of two consecutive records per device, where the two records are in the following form:
[Device $2$devnam] WWID = displayable_identifier |
During autoconfiguration, the Fibre Channel is probed and the WWIDs are fetched for all devices. If the fetched WWID matches an entry in the memory-resident copy of the SYS$DEVICES.DAT file, then the device is configured using the device name that has been paired with that WWID.
The SYS$DEVICES.DAT file is also used for port allocation class (PAC) information. Fibre Channel tape-naming is a second use of this same file, even though PACs and Fibre Channel tapes are not related, other than their common need to access file-based device information at boot time. By default, the SYS$DEVICES.DAT file is created in the cluster common directory, SYS$COMMON:[SYSEXE]. |
As an example, the following portion of SYS$DEVICES.DAT causes the eventual configuration of devices named $2$MGA300 and $2$MGA23:
! [Device $2$MGA300] WWID = 04100022:"COMPAQ DLT8000 JF71209240" ! [Device $2$mga23] WWID = 04100022:"DEC TZ89 (C) DECJL01164302" |
Although the file is typically read and written only by OpenVMS utilities, in rare instances you may need to edit the file. You can change only the unit number of the device, as described in Section 7.5.5. The internal syntax rules governing the file are summarized as follows:
Similarly, on the line containing WWID = , any white space (or none) can appear on either side of the equals sign. All lines must be left-justified, and all lines must be less than 512 characters.
The parsing of this file is not case sensitive, with one important exception: all characters enclosed within double quotation marks are taken literally, so that characters such as spaces and lowercase letters are significant. In the case of ASCII data enclosed by double quotation marks, there must be no space between the colon and the double quotation mark.
Also, if more than one WWID = line follows a single [Device devnam] line, the last WWID = value takes precedence. Normally, however, there is exactly one WWID = line per [Device devnam] line.
Similarly, if two or more [Device devnam] lines specify the same device name but different WWIDs, only the last device name and WWID specified in the file is used.
This file is read at boot time, and it is also read from and written to
by the SYSMAN IO FIND_WWID command. If there are additional
system-specific copies of the SYS$DEVICES.DAT file, their tape naming
records become automatically compatible as a result of running SYSMAN
IO FIND_WWID on each system. The SYSMAN IO FIND_WWID command is
described in more detail in the following section. The SYS$DEVICES.DAT
file may also be modified by the SYSMAN IO CREATE_WWID and REPLACE_WWID
commands which are described below.
7.5.3 Management Support for Fibre Channel Tape Devices
The following System Management utility (SYSMAN) commands are provided for managing Fibre Channel tape devices:
The following DCL support for Fibre Channel tape devices is available:
This section lists the steps required to configure a new tape or medium
changer on the Fibre Channel.
7.5.4.1 Basic Configuration Steps: Summary
The basic steps for configuring new Fibre Channel tape devices in a cluster are as follows:
$ MC SYSMAN SYSMAN> SET ENVIRONMENT/CLUSTER ! Execute on all nodes SYSMAN> IO FIND_WWID ! Assign names SYSMAN> IO AUTOCONFIGURE/LOG ! Configure devices SYSMAN> EXIT |
You need to perform these steps only once for the initial configuration. After any subsequent system reboot, the devices will appear automatically.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |