| Previous | Contents | Index |
The following figures show the qualifiers that can be used in BACKUP save, restore, copy, compare and list operations. The figures also indicate valid combinations of BACKUP qualifiers.
Figure G-1 Command Qualifiers Used in Save Operations
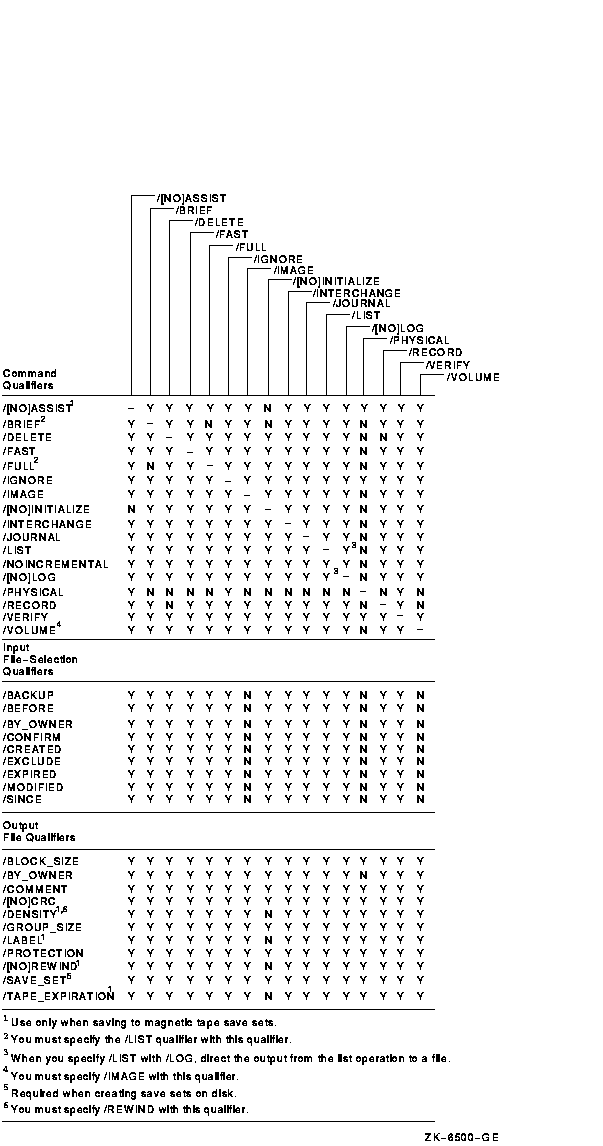
Figure G-2 Input File-Selection Qualifiers Used in Save Operations
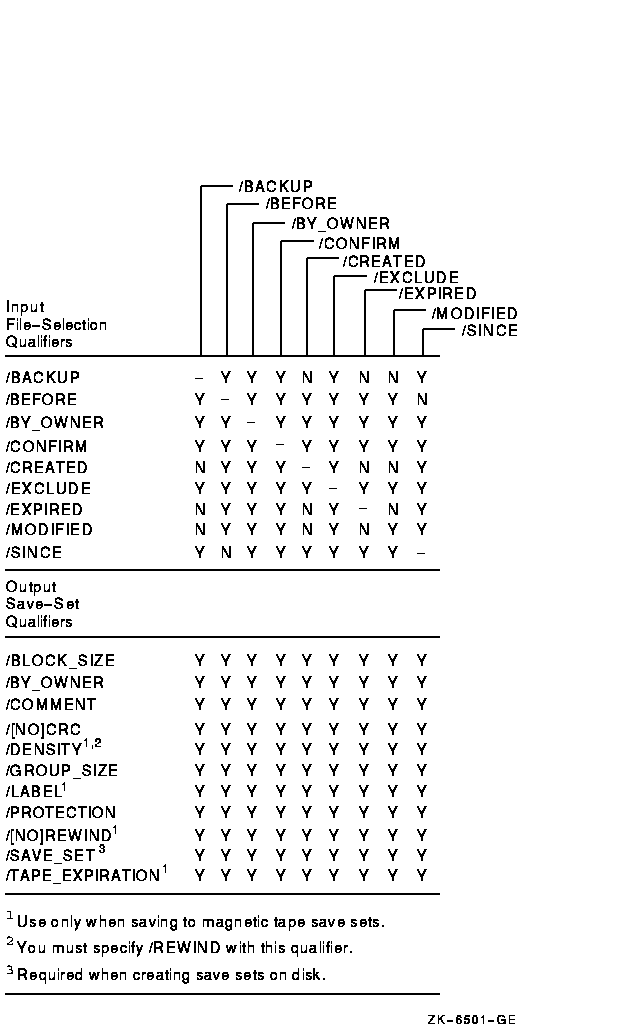
Figure G-3 Output Save-Set Qualifiers Used in Save Operations
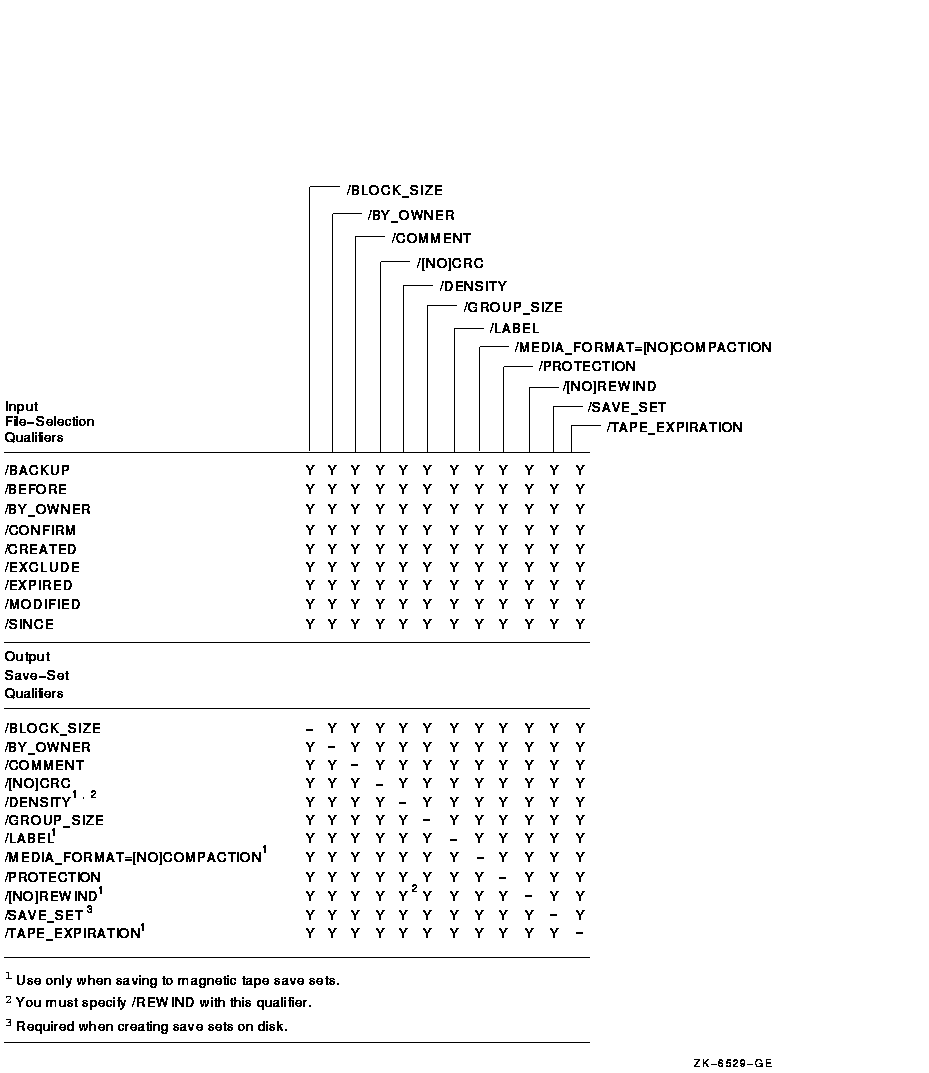
Figure G-4 Command Qualifiers Used in Restore Operations
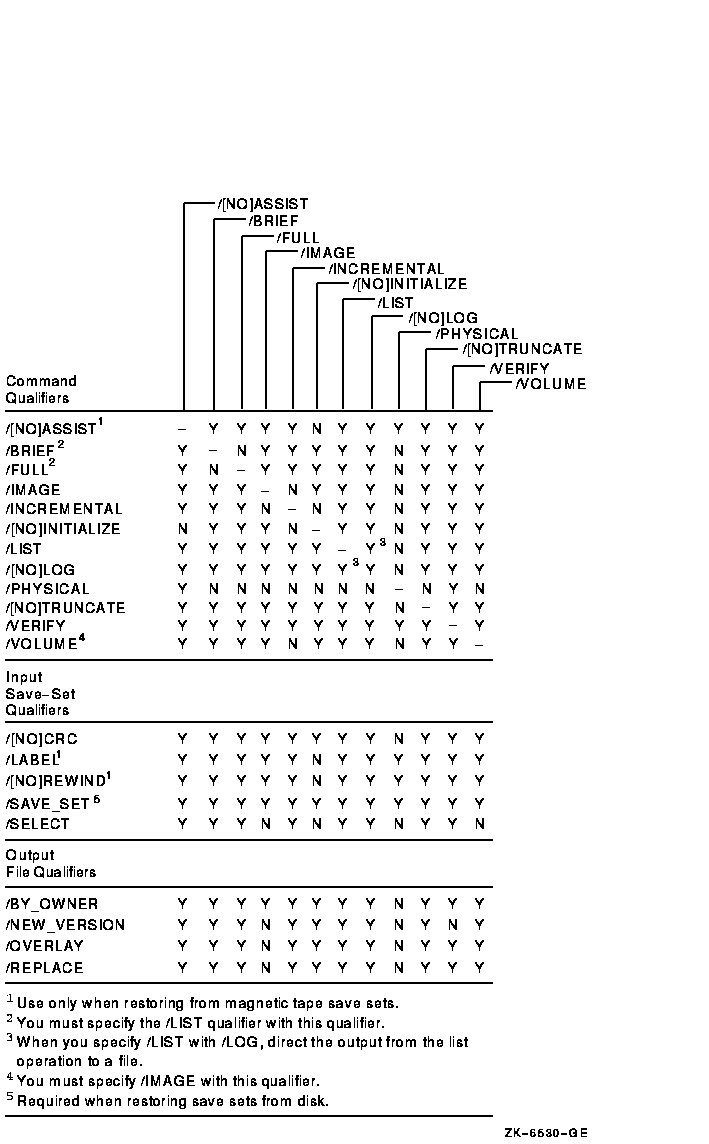
Figure G-5 Input Save-Set Qualifiers Used in Restore Operations
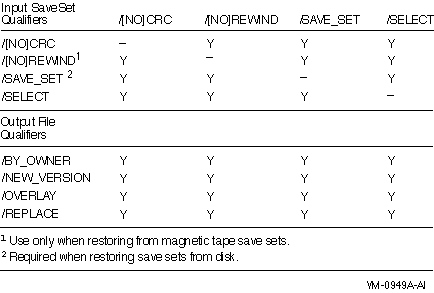
Figure G-6 Output File Qualifiers Used in Restore Operations
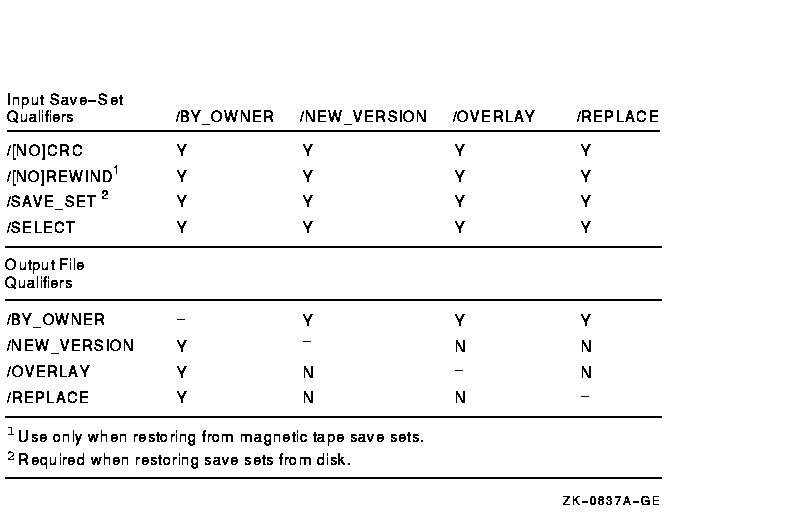
Figure G-7 Command Qualifiers Used in Copy Operations

Figure G-8 Input File-Selection Qualifiers Used in Copy Operations
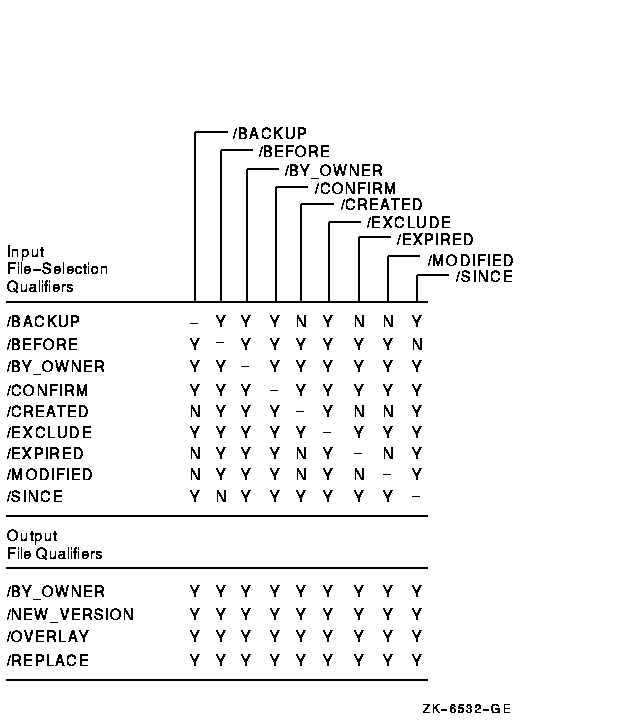
Figure G-9 Output File Qualifiers Used in Copy Operations
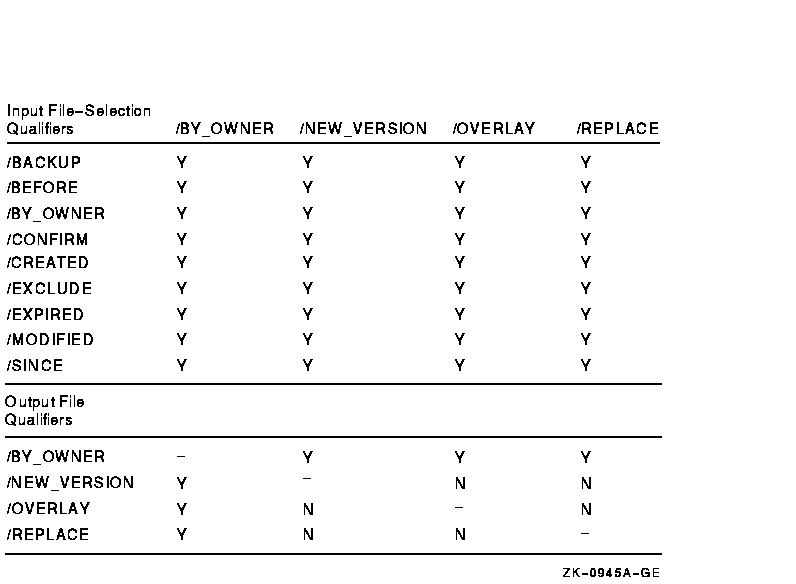
Figure G-10 Command Qualifiers Used in Compare Operations
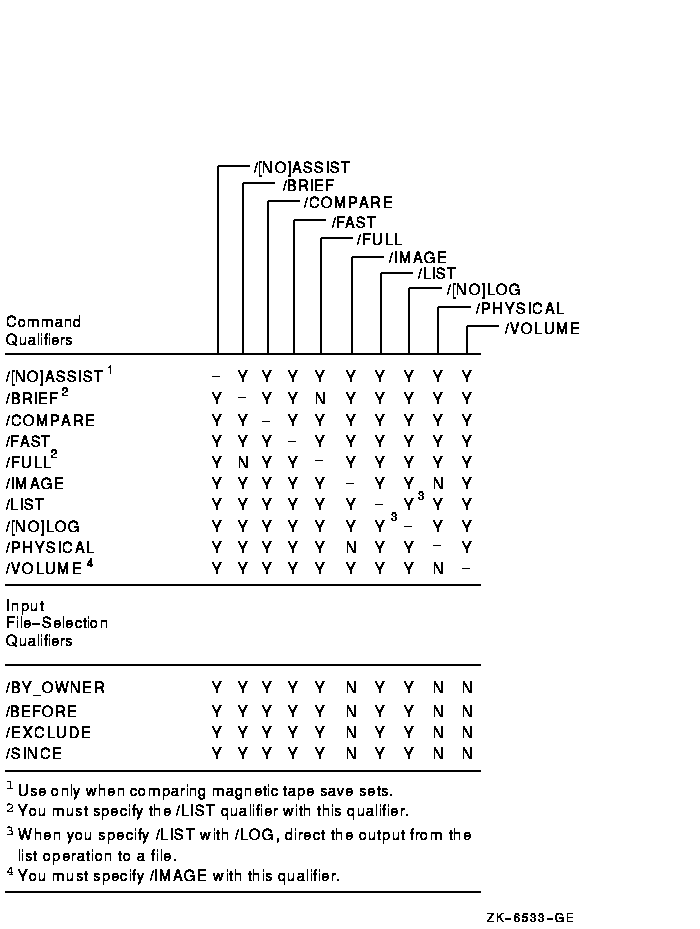
Figure G-11 Input File-Selection Qualifiers Used in Compare Operations
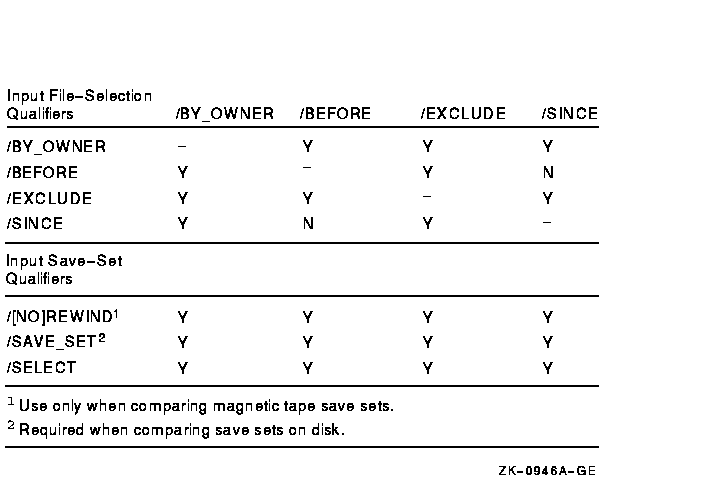
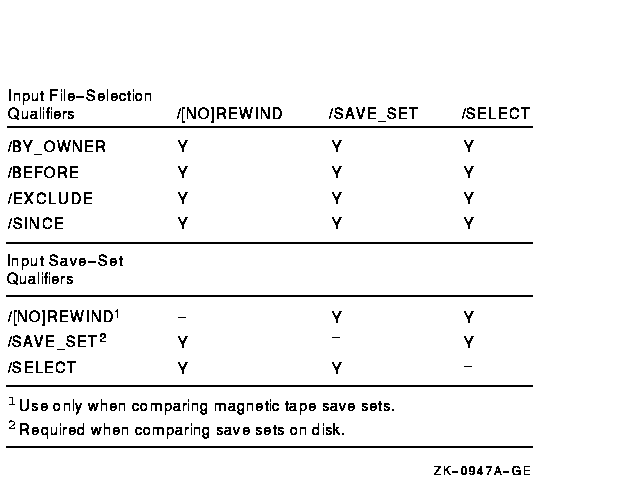
Figure G-12 Input Save-Set Qualifiers Used in Compare Operations
The following sections describe the MONITOR record formats.
Contact HP Customer Support to obtain the latest MONITOR record formats. |
Binary performance data is written into the MONITOR recording file when a MONITOR request indicates recording. A record is written to this file once per interval for each requested class. The record contains a predefined set of data for each of the requested performance classes.
The recording file is created when a MONITOR request is initiated, and is closed when the request terminates. The MONITOR recording file may be used as a source file to format and display the data on a terminal, to create a summary file, or to record a new recording file with different characteristics.
The record formats described in this section are subject to change without notice at any future OpenVMS release. |
The MONITOR recording file is an OpenVMS RMS sequential file with variable-length records. Each record in the file begins with a one-byte type field. The remaining fields are different in length and format for each record type. The following list contains three categories of record types:
Customer control records may appear anywhere in the recording file. They are not generated by MONITOR and are ignored by MONITOR when it reads the file.
The first records in the MONITOR recording file, excluding customer control records, are HP control records. The beginning of the file has three types of HP control records: the file header record, the system information record, and the record RMS file name record. Node transition records are also control records, but can appear anywhere in the file.
Class records, which contain data on requested performance classes, follow the HP control records. The class record is generally written once per interval for each class being recorded. An exception to this rule occurs when several class records are required to contain data for a single class over a single interval. This can occur for the PROCESSES class when too many processes exist to be accommodated by the maximum record size.
Unique numbers are assigned to each MONITOR record type. Record type numbers 0--127 are reserved for class records; numbers 128--191 are reserved for HP control records; numbers 192--255 are reserved for customer control records.
MONITOR generates 29 record types. The following table lists the MONITOR record types and their numbers, with associated class types. (For an explanation of MONITOR class types, see Section H.4.1.)
Beginning in OpenVMS Version 8.3, the header include file $MONDEF provides symbolic constant definitions for the class numbers. |
| Record Type | Type Number | Class Type |
|---|---|---|
| File Header | 128 | |
| System Information | 129 | |
| Node Transition | 130 | |
| RMS File Name | 131 | |
| PROCESSES Class | 0 | component |
| STATES Class | 1 | system |
| MODES Class | 2 | component |
| PAGE Class | 3 | system |
| IO Class | 4 | system |
| FCP Class | 5 | system |
| POOL Class 1 | 6 | system |
| LOCK Class | 7 | system |
| DECNET Class | 8 | system |
| RESERVED | 9 | system |
| RESERVED | 10 | system |
| FILE_SYSTEM_CACHE Class | 11 | system |
| DISK Class | 12 | component |
| RESERVED | 13 | component |
| DLOCK Class | 14 | system |
| SCS Class | 15 | component |
| RESERVED | 16 | system |
| SYSTEM Class | 17 | system |
| RESERVED | 18 | system |
| CLUSTER Class | 19 | system |
| RMS Class | 20 | component |
| MSCP_SERVER Class | 21 | system |
| TRANSACTION Class | 22 | system |
| VECTOR Class | 23 | component |
| VBS Class | 24 | system |
| RESERVED | 25 | system |
| RLOCK | 26 | system |
| TIMER | 27 | system |
| ALIGN | 28 | system |
The following sections define the contents of each field within each record type. Record type and record size are given in decimal representation. References to system time indicate time values in system time format (64-bit format).
The field offset names listed are not defined within MONITOR. However, HP recommends that you define and use these offset names when you work with MONITOR output records.
The following example is the suggested naming convention for the field offset names:
|
MNR_CCC$X_DDDDD |
CCC is a record type or class mnemonic.
X is a one-letter code indicating the size of the data item, as follows:
B for byte
W for word
L for longword
Q for quadword
O for octaword
T for ASCII string
DDDDD is the name describing the data item.
In the following tables that describe the record fields, the size of
the data is shown in parentheses following the description of the field
contents.
H.3 HP Control Records
The four types of HP control records are:
Each file has one header record, which contains information applicable to all classes of performance data contained in the file. It must be the first record (except for customer control records) in the file.
One system information record exists per node per file. The record
contains information about the system being monitored and follows the
header record in the file.
H.3.1 File Header Record
The file header record has a record type of 128 and a size of 259 bytes.
Figure H-1 illustrates the format of the file header record on Alpha and I64 systems.
Figure H-1 File Header Record Format - Alpha and I64
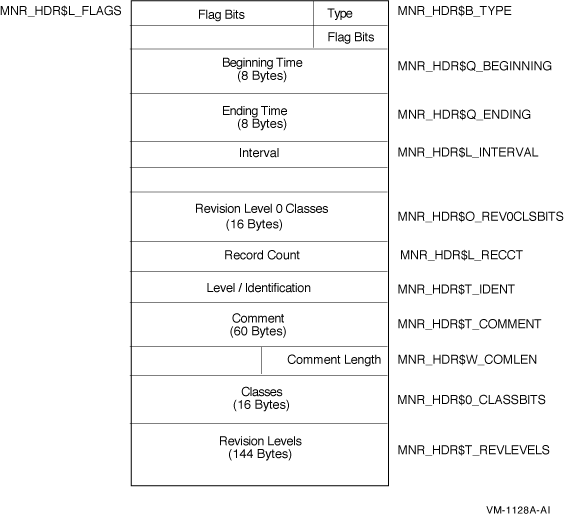
Figure H-2 illustrates the format of the file header record on VAX systems.
Figure H-2 File Header Record Format - VAX Only
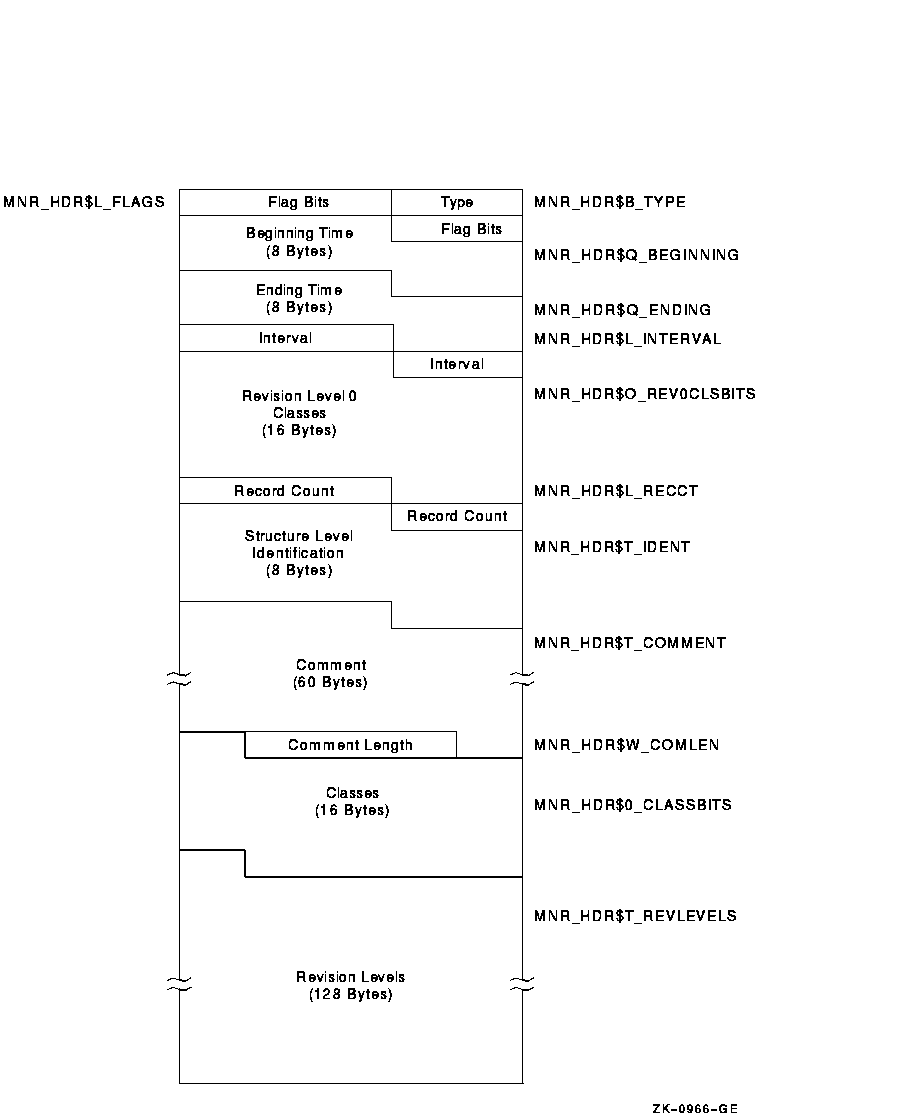
The following table describes the fields in the file header record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Type | MNR_HDR$B_TYPE | Record type identifier (1 byte). |
| Flags | MNR_HDR$L_FLAGS | Total of 32 flag bits; low-order bit = bit 0. All flags reserved to HP for future use (1 longword). |
| Beginning Time | MNR_HDR$Q_BEGINNING | System time of beginning of recording (1 quadword). |
| Ending Time | MNR_HDR$Q_ENDING | System time of end of recording (1 quadword). |
| Interval | MNR_HDR$L_INTERVAL | Interval in seconds between collections; this is the value specified by the user in the recording request. It is not necessarily equal to the exact interval value obtained by subtracting two consecutive time-stamps for a given class (1 longword). |
| Revision Level 0 Classes | MNR_HDR$O_REV0CLSBITS | A 128-bit string representing all classes; a bit set to 1 indicates the presence in this file of a class which is at revision level 0 and whose type number corresponds to the bit number. Low-order bit = bit 0 (1 octaword). This field is provided for compatibility with OpenVMS VAX Version 3.0 files. |
| Record Count | MNR_HDR$L_RECCT | Count of all records in the file (1 longword). |
| Structure Level Identification | MNR_HDR$T_IDENT | MONITOR Recording File Structure Level Identification (MON01060 for Version 8.3)(8 bytes). |
| Comment | MNR_HDR$T_COMMENT | Recording file description supplied by the user, including trailing blanks (60 bytes). |
| Comment Length | MNR_HDR$W_COMLEN | Actual length of recording file description string specified by the user (1 word). |
| Classes | MNR_HDR$O_CLASSBITS | A 128-bit string representing all classes; a bit set to 1 indicates the presence in this file of the class whose type number corresponds to the bit number. Low-order bit = bit 0 (1 octaword). |
| Revision Levels | MNR_HDR$T_REVLEVELS | A 128-byte string consisting of a one-byte binary revision level number for each class. A class has a revision level of 0 initially. For each MONITOR release, if the record definition has changed, the revision level will be increased (not necessarily by 1). |
H.3.2 System Information Record
The system information record has a record type of 129 and a size of 47
bytes. Figure H-3 illustrates the format of the system information
record on Alpha and I64 systems.
Figure H-3 System Information Record Format - Alpha and I64
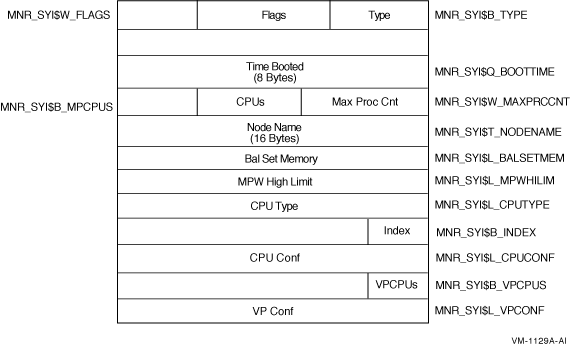
Figure H-4 illustrates the format of the system information record on VAX systems.
Figure H-4 System Information Record Format - VAX Only
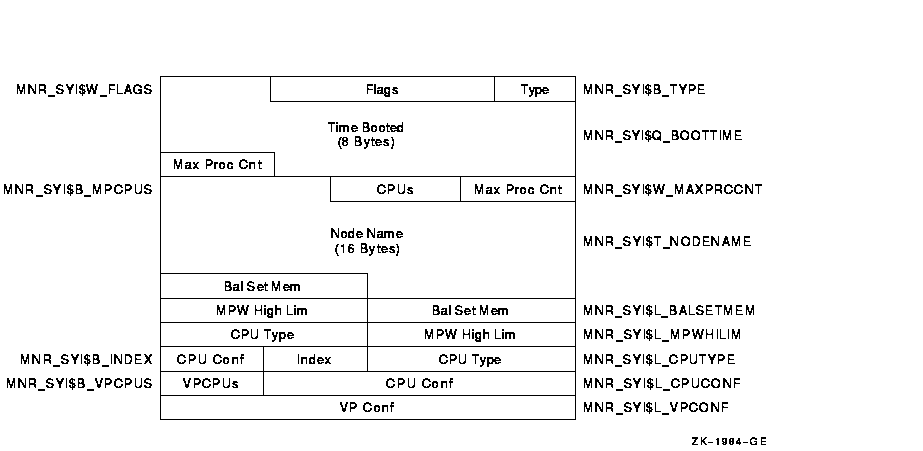
The following table describes the fields in the system information record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Type | MNR_SYI$B_TYPE | Type identifier (1 byte). |
| Flags | MNR_SYI$W_FLAGS | Total of 16 flag bits; low-order bit = bit 0. If bit 0 is set to 1, the node on which the data was collected is a member of a VAXcluster. All other flags reserved to HP for future use (1 word). |
| Time Booted | MNR_SYI$Q_BOOTTIME | System time at which system booted. MONITOR calculates this time by taking the number of seconds since system boot, converting this to a negative value, and adding it to the current system time (1 quadword). |
| Max Process Cnt | MNR_SYI$W_MAXPRCCNT | MAXPROCESSCNT system parameter value (1 word). |
| CPUs | MNR_SYI$B_MPCPUS | Number of CPUs (1 byte). |
| Node Name | MNR_SYI$T_NODENAME | Node name of node being monitored (counted ASCII string, 16 bytes). |
|
Balance Set
Memory (Bal Set Mem) |
MNR_SYI$L_BALSETMEM | Number of process pages to which memory can be allocated (1 longword). |
|
MPW High
Limit |
MNR_SYI$L_MPWHILIM | MPW_HILIMIT system parameter value (1 longword). |
| CPU Type | MNR_SYI$L_CPUTYPE | CPU type code. Use $PRDEF macro for code values (1 longword). |
| Index | MNR_SYI$B_INDEX | Identifies the position of this node in several internal MONITOR data structures (1 byte). |
| CPU Config | MNR_SYI$L_CPUCONF | Bit mask defining the location of each CPU in a multiprocessor (1 longword). |
| VPCPUs | MNR_SYI$B_VPCPUS | Number of vector-present processors in the current system (1 byte). |
| VP Config | MNR_SYI$L_VPCONF | Bit mask identifying the vector-present processors in the configuration (1 longword). |
The node transition record has a record type of 130 and a size of 2 bytes. Figure H-5 illustrates the format of the node transition record.
Figure H-5 Node Transition Record Format
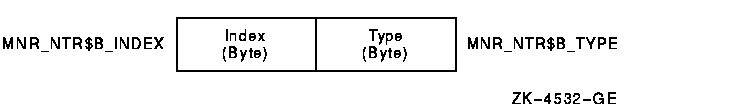
The following table describes the fields in the node transition record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Type | MNR_NTR$B_TYPE | Record type identifier---indicates node removal operation (1 byte). |
| Index | MNR_NTR$B_INDEX | Identifies the position of this node in several internal MONITOR data structures (1 byte). |
The RMS file record has a record type of 131 and a variable size that depends on the number of RMS files and length of the file name string. Figure H-6 illustrates the format of the RMS file record.
Figure H-6 RMS File Record Format
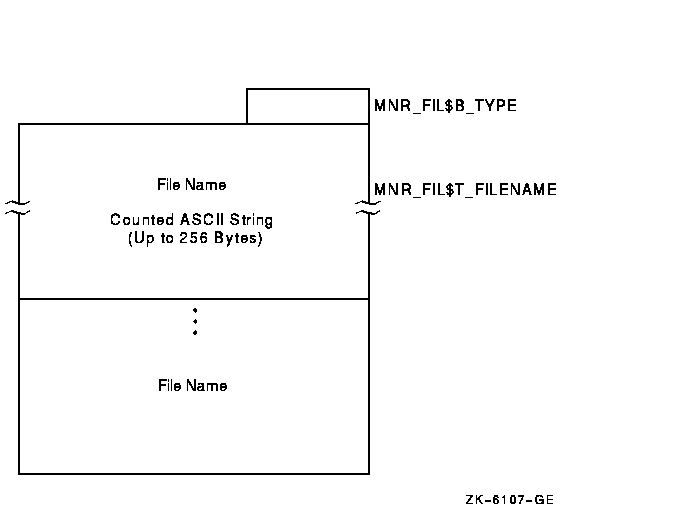
The following table describes the fields in the RMS file record.
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Type | MNR_FIL$B_TYPE | Record type identifier (1 byte). |
| Filename | MNR_FIL$T_FILENAME | A counted ASCII string that identifies the RMS file for MONITOR RMS requests (up to 256 bytes). |
The MONITOR recording file contains one class record for each requested
class for every collection interval, except for the PROCESSES class.
(See Section H.4.2.12 for more information about the PROCESSES class
records.) For example, if a MONITOR user requested to record five
classes (excluding PROCESSES) for a duration of 100 collection
intervals, the file would contain 500 class records. Class records
occur in order of increasing type number within an interval. The first
class record for a given interval follows the last class record for the
previous interval.
H.4.1 Class Type Formats
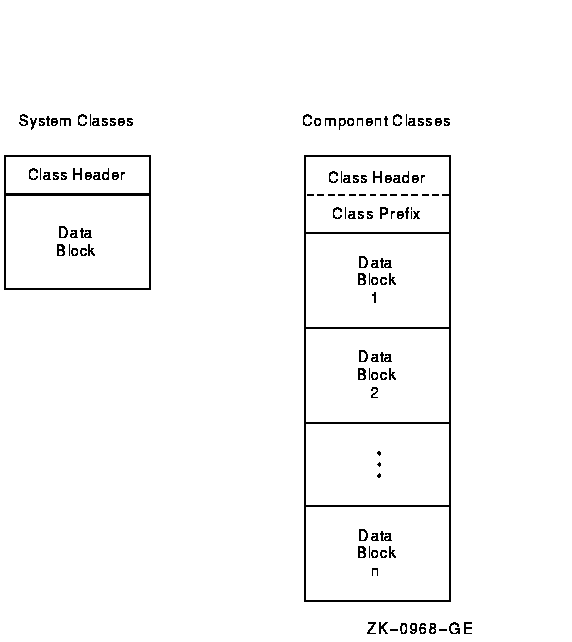
The two basic class types are system classes and component classes. A class record for a system class generally consists of counts for systemwide activities (such as page faults), whereas a class record for a component class normally contains a count for each element of a measured activity (such as I/O operations for each disk in the system).
Specifically, a class record for a system class consists of a class header followed by a data block. A class record for a component class has a class header followed by a class prefix and one data block per element.
Figure H-7 illustrates the format for class records.
Figure H-7 Class Record Format
The class header is the first part of every class record. Its format is independent of class. On Alpha and I64 systems, the class header is 16 bytes long; on VAX systems, the class header is 13 bytes long.
Figure H-8 illustrates the format of the class header on Alpha and I64 systems.
Figure H-8 Class Header Format - Alpha and I64
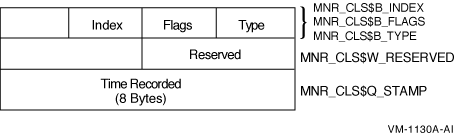
Figure H-9 illustrates the format of the class header on VAX systems.
Figure H-9 Class Header Format - VAX Only
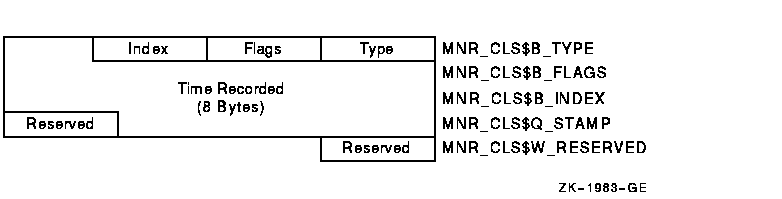
The following table describes the fields in the class header:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Type | MNR_CLS$B_TYPE | Record type identifier (1 byte). |
| Flags | MNR_CLS$B_FLAGS | Total of 8 flag bits; low order bit = bit 0. If bit 0 is set to 1, the data for this interval continues in the next record. Can be set for the PROCESSES class only. All other flags reserved by HP for future use (1 byte). |
| Index | MNR_CLS$B_INDEX | Identifies the position of this node in several internal MONITOR data structures (1 byte). |
| Time | MNR_CLS$Q_STAMP | System time at which this class record was recorded. The time value is nondecreasing across all class records in the file. |
| Reserved | MNR_CLS$W_RESERVED | Reserved for HP use (1 word). |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |