| Previous | Contents | Index |
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item descriptor:
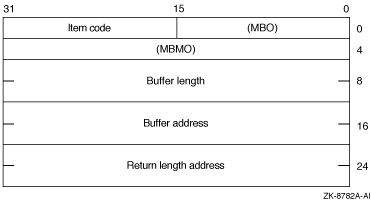
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item list entries:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| MBO | The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
| Item code | A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the information currently in the buffer, to be returned in the buffer, or to be returned by the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
| MBMO | The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
| Buffer address | A quadword containing the 64-bit address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
| Return length address | A quadword containing the 64-bit address of a word specifying the actual length (in bytes) of the information returned by $TRNLNM in the buffer pointed to by the buffer address field. |
LNM$_ACMODE
Returns the access mode that was associated with the logical name at the time of its creation. The buffer address field in the item descriptor is the address of a byte in which $TRNLNM writes the access mode.LNM$_ATTRIBUTES
Returns the attributes of the logical name and the equivalence name associated with the current LNM$_INDEX value.The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword bit mask wherein each bit corresponds to an attribute. The $TRNLNM service sets the corresponding bit for each attribute possessed by either the logical name or the equivalence name.
The $LNMDEF macro defines the following symbolic names for these attributes:
Attribute Description LNM$M_CONCEALED If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the equivalence name at the current index value for the logical name is a concealed logical name, as interpreted by OpenVMS RMS. LNM$M_CONFINE If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is not copied from a process to any of its spawned subprocesses. The DCL command SPAWN creates subprocesses. LNM$M_CRELOG If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name was created using the $CRELOG system service. LNM$M_EXISTS If $TRNLNM sets this bit, an equivalence name with the specified index does exist. LNM$M_NO_ALIAS If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the name of the logical name cannot be given to another logical name defined in the same table at an outer access mode. LNM$M_TABLE If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is the name of a logical name table. LNM$M_CLUSTERWIDE If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the logical name is in a clusterwide table. LNM$M_TERMINAL If $TRNLNM sets this bit, the equivalence name for the logical name cannot be subjected to further (recursive) logical name translation. LNM$_CHAIN
Processes another item list immediately following the current item list. The LNM$_CHAIN item code must be the last one in the current item list. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to the next item list.You can chain together 32-bit and 64-bit item lists.
LNM$_INDEX
Searches for an equivalence name that has the specified index value. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a longword containing a user-specified integer in the range 0 to 127.If you do not specify this item code, the implied value of LNM$_INDEX is 0 and $TRNLNM returns information about the equivalence name at index 0.
Because a logical name can have more than one equivalence name and each equivalence name is identified by an index value, you should specify the LNM$_INDEX item code first in the item list, before specifying LNM$_STRING, LNM$_LENGTH, or LNM$_ATTRIBUTES. These item codes return information about the equivalence name identified by the current index value, LNM$_INDEX.
LNM$_LENGTH
Returns the length of the equivalence name string corresponding to the current LNM$_INDEX value. The buffer address field in the item descriptor is the address of the longword in which $TRNLNM writes this length.If an equivalence name does not exist at the current LNM$_INDEX value, $TRNLNM returns the value 0 to the longword pointed to by the return length field of the item descriptor.
LNM$_MAX_INDEX
Each equivalence name for the logical name has an index associated with it. When you specify LNM$_MAX_INDEX, $TRNLNM returns a value equal to the largest equivalence name index. The buffer address field in the item descriptor is the address of a longword in which $TRNLNM writes this value. If the logical name exists but has no equivalence name (and, therefore, no index value), $TRNLNM returns a value of --1.LNM$_STRING
Returns the equivalence name string corresponding to the current LNM$_INDEX value. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to a buffer containing this string. The return length address field of the item descriptor contains an address of a word that contains the length of this string in bytes. The maximum length of the equivalence name string is 255 characters.If an equivalence name does not exist at the current LNM$_INDEX value, $TRNLNM returns the value 0 in the return length address field of the item descriptor.
LNM$_TABLE
Returns the name of the table containing the logical name being translated. The buffer address field of the item descriptor points to the buffer in which $TRNLNM returns this name. The return length address field of the item descriptor specifies the address of a word in which $TRNLNM writes the size of the table name. The maximum length of the table name is 31 characters.
The Translate Logical Name service returns information about a logical name. You need read access to a shareable logical name table to translate a logical name located in that shareable logical name table.For conventions regarding logical names for process-permanent files, see the chapter "Logical Name Services" in the HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
Read access is required.
None
$ADJSTK, $ADJWSL, $CRELNM, $CRELNT, $CRETVA, $CRMPSC, $DELLNM, $DELTVA, $DGBLSC, $EXPREG, $LCKPAG, $LKWSET, $MGBLSC, $PURGWS, $SETPRT, $SETSTK, $SETSWM, $ULWSET, $UPDSEC, $UPDSECW
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. An equivalence name for the logical name has been found. SS$_ACCVIO The service cannot access the location or locations specified by one or more arguments. SS$_BADPARAM One or more arguments have an invalid value, or a logical name table name or logical name was not specified. Or, an item list containing both 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries was found. SS$_BUFFEROVF The service completed successfully. The buffer length field in an item descriptor specified an insufficient value, so the buffer was not large enough to hold the requested data. SS$_IVLOGNAM The tabnam argument or lognam argument specifies a string whose length is not in the required range of 1 through 255 characters. SS$_IVLOGTAB The tabnam argument does not specify a logical name table. SS$_NOLOGNAM The logical name was not found in the specified logical name table or tables. SS$_NOPRIV The caller lacks the necessary privilege to access the specified name. SS$_TOOMANYLNAM Logical name translation of the table name exceeded the allowable depth (10 translations).
The Truncate service shortens a sequential file.For additional information about this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
Simulates the occurrence of a cluster configuration event to test the functionality of the notification AST.
SYS$TSTCLUEVT [handle] ,[acmode] ,[event]
int sys$tstcluevt (unsigned int *handle, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int event);
handle
OpenVMS usage: identifier type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Identification of the asynchronous system trap (AST) to be tested. The handle argument uniquely identifies the request and is returned when the $SETCLUEVT service is called.acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode for which a configuration event AST is to be triggered. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode.Each access mode has a symbolic name. The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access modes:
Symbol Access Mode PSL$C_KERNEL Kernel PSL$C_EXEC Executive PSL$C_SUPER Supervisor PSL$C_USER User event
OpenVMS usage: event_code type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Event code indicating the type of configuration for which an AST is to be triggered.Each event type has a symbolic name. The $CLUEVTDEF macro defines the following symbolic names:
Symbolic Name Description CLUEVT$C_ADD One or more OpenVMS nodes have been added to the OpenVMS Cluster system. CLUEVT$C_REMOVE One or more OpenVMS nodes have been removed from the OpenVMS Cluster system.
The Test Cluster Event service simulates the occurrence of a cluster configuration event to test the functionality of the notification ASTs. The service allows an application to test itself and must be issued from within the same process as the application being tested. $TSTCLUEVT does not affect other processes in the cluster.The service will allow one specific AST to be fired via the handle argument, or all ASTs for a specific configuration event via the event argument. Specifying both the event and the handle arguments will return an error.
If the handle argument is specified, the value of the acmode argument must not be greater than the access mode of the caller and must match the mode specified when the $SETCLUEVT service was called.
If the event argument is specified, those ASTs that match the value specified in the acmode argument, or that match the caller's mode, will be triggered.
None
None
$CLRCLUEVT, $SETCLUEVT
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_BADPARAM There is an unsatisfactory combination of event and handle parameters, or the event was specified incorrectly. SS$_NOSUCHOBJ No request was found that matches the description supplied.
Unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked and deleted at image exit.
SYS$ULKPAG inadr ,[retadr] ,[acmode]
int sys$ulkpag (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode);
inadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Starting and ending virtual addresses of the pages to be unlocked. The inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored. If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, a single page is unlocked.
If more than one page is being unlocked and you need to determine specifically which pages had been previously unlocked, you should unlock the pages one at a time, that is, one page per call to $ULKPAG. The condition value returned by $ULKPAG indicates whether the page was previously unlocked.
retadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference---array reference or descriptor
Starting and ending process virtual addresses of the pages actually unlocked by $ULKPAG. The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.If an error occurs while multiple pages are being unlocked, retadr specifies those pages that were successfully unlocked before the error occurred. If no pages were successfully unlocked, both longwords in the retadr array contain the value --1.
acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the symbols for the four access modes.The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
The Unlock Pages from Memory service unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG) service. Locked pages are automatically unlocked and deleted at image exit.On Alpha and I64 systems, if you are attempting to unlock executable code, you should issue multiple $ULKPAG calls: one to unlock the code pages and others to unlock the linkage section references to these pages.
To call the $ULKPAG service, a process must have PSWAPM privilege.
None
For more information, see the chapter about memory management in the HP OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
SS$_WASCLR The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously unlocked. SS$_WASSET The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously locked. SS$_ACCVIO The input array cannot be read by the caller; the output array cannot be written by the caller; or a page in the specified range is inaccessible or does not exist.
On Alpha and I64 systems, unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG_64) service.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$ULKPAG_64 start_va_64 ,length_64 ,acmode ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64
int sys$ulkpag_64 (void *start_va_64, unsigned __int64 length_64, unsigned int acmode, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64);
start_va_64
OpenVMS usage: address type: quadword address access: read only mechanism: by value
The starting virtual address of the pages to be unlocked. The specified virtual address will be rounded down to a CPU-specific page boundary.length_64
OpenVMS usage: byte count type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Length of the virtual address space to be unlocked. The specified length will be rounded up to a CPU-specific page boundary so that it includes all CPU-specific pages in the requested range.acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode on behalf of which the request is being made. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode.The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the four access modes:
Value Symbolic Name Access Mode 0 PSL$C_KERNEL Kernel 1 PSL$C_EXEC Executive 2 PSL$C_SUPER Supervisor 3 PSL$C_USER User The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. To unlock any specified page, the resultant access mode must be equal to or more privileged than the access mode of the owner of that page.
return_va_64
OpenVMS usage: address type: quadword address access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The lowest process virtual address of the unlocked virtual address range. The return_va_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the virtual address.return_length_64
OpenVMS usage: byte count type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The length of the virtual address range unlocked. The return_length_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword into which the service returns the length of the virtual address range in bytes.
The Unlock Pages from Memory service unlocks pages that were previously locked in memory by the Lock Pages in Memory ($LCKPAG_64) service.If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the return_va_64 and return_length_64 arguments.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully unlocked before the error occurred. If no pages were unlocked, the return_va_64 argument will contain the value -1, and a value cannot be returned in the memory location pointed to by the return_length_64 argument.
To call the $ULKPAG_64 service, a process must have PSWAPM privilege.
None
$LCKPAG_64, $ULKPAG
SS$_WASCLR The service completed successfully. At least one of the specified pages was previously unlocked. SS$_WASSET The service completed successfully. All of the specified pages were previously locked in the working set. SS$_ACCVIO The return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller, or an attempt was made to unlock pages by a caller whose access mode is less privileged than the access mode associated with the pages.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |