| Previous | Contents | Index |
On Alpha and I64 systems, retrieves attribute values from a persona (and accompanying extensions).
SYS$PERSONA_QUERY persona ,itmlst
int sys$persona_query (unsigned int *persona, void *itmlst);
persona
OpenVMS usage: persona type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is written.Two special values for persona are also permitted: 0, which means use the current persona, and -1, which means use the process' natural persona.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Attributes describing which information about the persona is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information or an item list processing directive. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword value of 0.The following diagram shows the format of a single item descriptor:
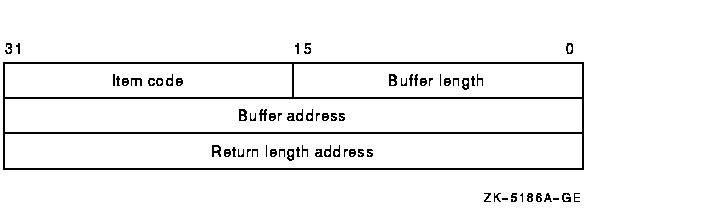
The following table lists the item field descriptors and their definitions:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Buffer length |
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in
bytes) of the buffer into which $PERSONA_QUERY writes the information.
The length of the buffer depends on the item code specified in the item
code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too
small, $PERSONA_QUERY truncates the data.
If the buffer length is specified as 0, the service does not return any data in the buffer; instead, the service returns the size of buffer required to contain the data in the Return Length address. This allows run-time determination of the size of buffer needed to hold the requested information. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information $PERSONA_QUERY is to return, or specifying a directive for processing subsequent items. The $ISSDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Description section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer into which $PERSONA_QUERY writes the information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word into which the service writes the length in bytes of the information it returned. If the buffer length field is zero (0), then you must specify a return length address. |
The Query for Persona Data service returns the requested items in the buffers supplied.OpenVMS Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the OpenVMS persona extension data:
Item Code Use+ Size (bytes) Description ISS$_USERNAME Q,M,F 32 OpenVMS user name as text string ISS$_ACCOUNT Q,M,F 32 OpenVMS account name as text string ISS$_DOMAIN Q,F 32 OpenVMS SCSNODE as text string as obtained from $GETJPI's nodename ISS$_PRINCIPAL Q,F 64 OpenVMS user name as text string ISS$_EXTENSION Q,F 32 The text string VMS ISS$_WORKPRIV Q,M 8 Working privilege mask ISS$_WORKCLASS Q,M Varying Working classification ISS$_RIGHTS Q Varying Enabled list of rights identifiers ISS$_NOAUDIT Q,M 4 No audit counter---0 means audits disabled ISS$_UIC Q,M,F 4 Current UIC ISS$_AUTHPRIV Q,M 8 Authorized privilege mask ISS$_PERMPRIV Q,M 8 Permanent privilege mask ISS$_IMAGE_WORKPRIV Q,M 8 Image working privilege mask ISS$_ENABLED Q 4 Mask of enabled rights chains ISS$_AUTHRIGHTS Q Varying Authorized list of rights identifiers ISS$_MINCLASS Q Varying Minimum classification ISS$_MAXCLASS Q Varying Maximum classification
Common Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the common persona extension data:
| Item Code | Use+ | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_COMMON_USERNAME | Q | varying | User name as text string |
| ISS$_COMMON_ACCOUNT | Q | varying | Account name as text string |
| ISS$_COMMON_FLAGS | Q | 4 | Flags as a longword |
| ISS$_DOMAIN | Q | varying | Domain name as text string |
| ISS$_COMMON_PRINCIPAL | Q | varying | Principal name as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q | 32 | Extension name as text string |
| ISS$_DOI | Q | 8 | Domain Of Interpretation quadword |
General Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the general persona extension data:
| Item Code | Use+ | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_SWITCH_EXTENSION | Q,M | 4 | Extension ID to be used for subsequent item code processing |
| ISS$_FLAGS | Q,M | 4 | Various flags (ISS$_FLAG_PERMANENT) |
| ISS$_MODE | Q | 4 | Persona creation mode (user, supervisor, exec, or kernel) |
| ISS$_UID | Q | 16 | UID assigned when persona created |
| ISS$_PERSONA_ID | Q | 4 | Persona ID of this PSB |
| ISS$_PRIMARY_EXTENSION | Q,M | 4 | Extension id of primary authenticator |
| ISS$_EXTENSION_COUNT | Q | 4 | Count of extensions attached to persona |
| ISS$_EXTENSION_ARRAY | Q | varying | Array of longwords containing extension ids of all extensions attached to persona |
NT Persona Item Codes
The following table contains the item codes specific to the NT persona extension data:
| Item Code | Use+ | Size (bytes) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISS$_NT_PRINCIPAL | Q,F | varying | Principal name as text string |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_USERNAME | Q,F | varying | NT user name as text string |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_DOMAINNAME | Q,F | varying | NT domain as text string |
| ISS$_EXTENSION | Q,F | varying | The text string "NT" |
| ISS$_NT_FLAGS | Q,M | 4 | Various flags |
| ISS$_NT_USER_REFCOUNT | Q,M | 4 | NT-Specific User Field |
| ISS$_NT_CREDENTIALS | Q,M | varying | All Token and Security info |
| ISS$_NT_NT_OWF_PASSWORD | Q,M | varying | NT Password |
| ISS$_NT_LM_OWF_PASSWORD | Q,M | varying | LM Password |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_USERSESSIONKEY | Q,F | 16 | User's session key |
| ISS$_NT_TOKEN_LMSESSIONKEY | Q,F | 8 | LM session key |
No privileges are required to call this service.
None
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer length or buffer cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM An invalid parameter was specified. SS$_BADITMCOD The item list contains an invalid item code. SS$_NOSUCHEXT The extension requested does not exist on the system. SS$_PERSONANONGRATA The persona ID supplied is invalid.
On Alpha and I64 systems, reserves a persona ID in the server's persona table to be filled in by the $PERSONA_DELEGATE system service.
SYS$PERSONA_RESERVE clientPID ,persona
int sys$persona_reserve (unsigned int *clientPID, unsigned int *persona);
clientPID
OpenVMS usage: process_ID type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword containing the External Process Identification (EPID) of the client process for which the server is reserving the slot.persona
OpenVMS usage: persona type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword into which the persona identification is written. This service sets aside the identification for the client's to-be-delegated persona.
This service reserves a persona identifier slot within the current process for a specific client process to use in delegating its persona to this process. A reserved persona slot can be deleted by a call to the $PERSONA_DELETE service. When a return fails, no persona slot has been reserved for the client process.The delegation of persona is only supported for processes residing on the same node of a cluster.
IMPERSONATE
BYTLM
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The item list cannot be read by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM An invalid parameter was specified. SS$_EXQUOTA The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona. SS$_NONEXPR The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified.
On Alpha and I64 systems, allows modification of the CPU affinity set for a specified kernel thread.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY [pidadr], [prcnam], [select_mask], [modify_mask], [prev_mask], [flags] [,[mask_length]]
int sys$process_affinity (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *select_mask, struct _generic_64 *modify_mask, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags,...);
pidadr
OpenVMS usage: process_id type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose affinity mask is to be modified or returned. The pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.Process selection is made through a combination of the pidadr and prcnam arguments. If neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service operations are made to the user affinity mask of the current kernel thread of the calling process. The pidadr argument takes precedence over the prcnam argument in any circumstances where both are supplied in the service call.
prcnam
OpenVMS usage: process_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Process name of the process whose affinity mask is to be modified or returned. The prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a character string descriptor pointing to the process name string. A process can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. The service operations are made to the user affinity mask of the initial thread of the specified process.If pidadr and prcnam are both specified, then pidadr is modified or returned and prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified, then the context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is modified or returned.
select_mask
OpenVMS usage: bitmap type: quadword bitmap access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The select-mask argument specifies which bits of the specified process's affinity mask are to be modified. The select_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding CPU position in the mask is to be modified.modify_mask
OpenVMS usage: bitmap type: quadword bitmap access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Mask specifying the settings for those explicit affinities selected in the select_mask argument. The modify_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding CPU is to be added to the specified process affinity set; when clear, the corresponding CPU is to be removed from the specified process affinity set.To add a specific CPU to the affinity mask set, that bit position must be set in both select_mask and modify_mask. To remove a specific CPU from the affinity mask set, that bit position must be set in select_mask and clear in modify_mask.
The constant CAP$K_ALL_CPU_ADD, when specified in modify_mask, indicates that all CPUs specified in select_mask are to be added to the affinity mask set. The constant CAP$K_ALL_CPU_REMOVE indicates that all CPUs in select_mask are to be removed from the affinity mask set.
prev_mask
OpenVMS usage: bitmap type: quadword bitmap access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Previous CPU affinity mask for the specified kernel thread before execution of this call to $PROCESS_AFFINITY. The prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword into which $PROCESS_AFFINITY writes the previous explicit affinity bitmap.flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Options selected for affinity modification. The flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an option. Only the bits specified below are used; the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved and must be 0.Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines. The flags argument is constructed by performing a logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
The following table describes the symbolic name of each option:
Symbolic Name Description CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT Indicates whether to modify the permanent process affinities in addition to the current image copy. If CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT is set, then both the permanent and current affinities are modified. If the flag bit is clear or flags is unspecified, then just the current image process affinities are modified. This bit also determines which of the affinity masks are returned in prev_mask. If set, the permanent mask, used to reinitialize the current set at image rundown, is returned. If the bit is clear or the flags argument is not specified, the current running mask is returned.
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a nonrunnable state under some circumstances. No operation of this service will allow a transition from a runnable to blocked state; however, if the kernel thread is already at a blocked state, this bit determines whether the result of the operation must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU is set or flags is unspecified, the kernel thread will be checked to ensure it can safely run on one of the CPUs in the active set; otherwise, any valid state operations on kernel threads already in a blocked state will be allowed. CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU_ACTIVE Indicates whether a check is made to verify that all CPUs in the select mask that are about to be selected for affinity binding are in the active set. This does not apply to CPUs that are about to be cleared from the current affinity set. Unlike CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU where only a single CPU has to be valid for the condition to pass, CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU_ACTIVE requires that all CPUs in the selected set must pass the criteria. CAP$M_PURGE_WS_IF_NEW_RAD Causes the working set of the process to be purged if the choice of affinity results in a change to the home RAD of the process.
mask_length
OpenVMS usage: bitmap type: quadword bitmap access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The mask_length specifies the length in bytes of each of the three bitmaps: select_mask, modify_mask, prev_mask. If mask_length is not supplied or specified as zero, a length of 8 bytes is used.The correct value for mask_length is determined by the number of supported CPUs on the system. You can compute the number of bytes needed for the bitmap as follows: Use the $GETSYI system service with an item code of SYI$_MAX_CPUS to find the minimum number of bits needed, round this number up to a multiple of 64, and divide the result by 8.
The Modify Process Affinity system service, based on the arguments select_mask and modify_mask, adds or removes CPUs from the specified kernel thread's affinity mask sets. If specified, the previous affinity mask is returned in prev_mask. With the modify_mask argument, multiple CPUs can be added to or removed from the process affinity mask set in the same system service call.Adding a specific CPU to the process affinity mask indicates that the kernel thread is able to execute only on that CPU or on the others specified in the mask. Affinity scheduling takes effect as soon as the affinity mask becomes nonzero, limiting the CPU selection for the kernel thread to what is specified and available. Thread selection and execution is still subject to standard capability requirements, but only the affinity CPU set is considered when looking for an available site. When the affinity mask is cleared, all CPUs are again considered available and affinity is deactivated.
Either modify_mask or prev_mask, or both, must be specified as arguments. If modify_mask is specified, then select_mask must be specified as an argument. If modify_mask is not specified, then no modifications are made to the affinity mask for the specified kernel thread. In this case, select_mask is ignored. If prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask is returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU bit in the flags argument requires that the final thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise, interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread is already in one.
Previous Next Contents Index