| Previous | Contents | Index |
For example, if the input buffer contains the values 5 and 3, INIT_VOL starts at logical block number 5 and allocates 3 blocks.
The number of entries in the buffer is determined by the buffer length field in the item descriptor.
All media supplied by HP and supported on the operating system, except disks and TU58 cartridges, are factory formatted and contain bad block data. The Bad Block Locator utility (BAD) or the diagnostic formatter EVRAC can be used to refresh the bad block data or to construct it for the disks and TU58 cartridges. The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN item code is necessary only to enter bad blocks that are not identified in the volume's bad block data. For more information, see the OpenVMS Bad Block Locator Utility Manual (available on the Documentation CD-ROM).
The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_LBN item code applies only to disks.
The input buffer must contain an array of octawords containing information in the following format:
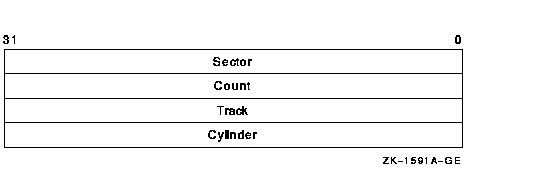
The following table describes the information to be specified for INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sector | INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_SECTOR | Specifies the sector number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
| Count | INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_COUNT | Specifies the number of blocks to be allocated. |
| Track | INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_TRACK | Specifies the track number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
| Cylinder | INIT$L_BADBLOCKS_CYLINDER | Specifies the cylinder number of the first block to be marked as allocated. |
For example, if the input buffer contains the values 12, 3, 1, and 2, INIT_VOL starts at sector 12, track 1, cylinder 2, and allocates 3 blocks.
The number of entries in the buffer is determined by the buffer length field in the item descriptor.
All media supplied by HP and supported on the operating system, except disks and TU58 cartridges, are factory formatted and contain bad block data. The Bad Block Locator utility (BAD) or the diagnostic formatter EVRAC can be used to refresh the bad block data or to construct it for the disks and TU58 cartridges. The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC item code is necessary only to enter bad blocks that are not identified in the volume's bad block data. For more information, see the OpenVMS Bad Block Locator Utility Manual.
The INIT$_BADBLOCKS_SEC item code applies only to disks.
volume size in blocks/(255 * 4096)
The INIT$_CLUSTERSIZE item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks (for Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks, the cluster size is 1). For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks, the cluster size default depends on the disk capacity:
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary. |
The INIT$_COMPACTION item code applies only to TA90 drives.
For magnetic tape volumes, the INIT$_DENSITY item code specifies the density.
The DENSITY item code is dependent on the type of tape device. If a tape device is seen as capable of using the MT3 density codes the buffer for MNT$_DENSITY item code must contain a longword with one of the MT3 codes, as defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET (MT3$K_TK50, MT3$K_3480, M53$K_DSDLT, MT3$K_AIT2 and so on). Refer to the MT3_SUPPORTED argument for $GETDVI.
If the device does not support MT3 densities, the buffer specifies the density in bytes per inch (bpi) at which the magnetic tape is written. The following are possible symbolic values for tapes:
The specified density value must be supported by the drive. If you do not specify a density item code for a blank magnetic tape, the system uses a default density of the highest value allowed by the tape drive. If the drive allows 6250, 1600, and 800 bpi operation, the default density is 6250. If the drive allows only 1600 and 800 bpi operation, the default density is 1600. If you do not specify a density item code for a magnetic tape that has been previously written, the system uses the previously set volume density.
For diskettes, the INIT$_DENSITY item code specifies how the diskette is to be formatted. Possible symbolic values for diskettes are as follows:
For disk volumes that are to be initialized on RX02, RX23, or RX33 diskette drives, the following values specify how the disk is to be formatted:
Diskettes are initialized as follows:
If you do not specify a density item code for a disk, the system leaves the volume at the density at which it was last formatted. RX02 disks purchased from HP are formatted in single density.
Disks formatted in double density cannot be read or written by the console block storage device (an RX01 drive) of a VAX-11/780 processor until they have been reformatted in single density. |
The INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code applies only to disks.
For disk devices, this item code sets the ERASE volume attribute, causing each file on the volume to be erased when it is deleted.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks, the buffer must contain a longword value in the range 0 to 65535. For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks, the input buffer must contain a longword value in the range of 0 to 255. The default value is 5 for both Structure Level 1 and Structure Level 2 disks.
The default extension set by this item code is used only if the following conditions are in effect:
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary. |
The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask on systems:
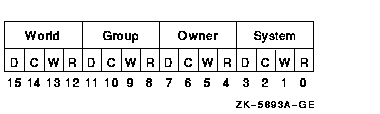
The INIT$_FPROT item code applies only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1 disks and is ignored if it is used on an OpenVMS system. OpenVMS systems use the default file extension set by the DCL command SET PROTECTION/DEFAULT.
The INIT$_HEADERS item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER disables FHM for a volume.
The INIT$_HIGHWATER and INIT$_NO_HIGHWATER item codes apply only to Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 disks.
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary. |
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code in conjunction with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING, INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE, or INIT$_INDEX_END results in an error. From DCL, if you specify INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK with INIT$_INDEX_BEGINNING, INIT$_INDEX_MIDDLE, or INIT$_INDEX_END, then INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
The INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK item code applies only to disks.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
When issuing calls to $INIT_VOL, using this item code with INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK results in an error. If you specify both item codes from DCL, INIT$_INDEX_BLOCK takes precedence.
This item code applies only to disks.
For more information about the INIT$_INTERCHANGE item code and about magnetic tape labeling and tape interchange, see the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual, Volume 1: Essentials.
! " % ' ( ) * + , - . / : ; < = >
By default, the operating system provides a routine SYS$MTACCESS that checks this field in the following manner:
volume size in blocks/cluster factor + 1
Once initialized, the maximum number of files can be increased only by reinitializing the volume.
The default maximum number of files is calculated as follows:
volume size in blocks/(cluster factor + 1) * 2
The INIT$_MAXFILES item code applies only to disks.
This item code applies to ODS-5 disks as well as to ODS-2 disks. For more information, see the INITIALIZE command in the HP OpenVMS DCL Dictionary. |
To specify INIT$_OVR_ACCESS, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
To specify INIT$_OVR_EXP, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
To specify INIT$_OVR_VOLO, the caller must either own the volume or have VOLPRO privilege.
For magnetic tapes, no UIC is written unless protection on the magnetic tape is specified. If the INIT$_VPROT item code is specified but the INIT$_OWNER item code is not specified, the UIC of the caller is assigned ownership of the volume.
The INIT$_READCHECK item code applies only to disks.
The default protection for a Structure Level 1 disk is full access to system, owner, and group users, and read access to all other users.
The INIT$_STRUCTURE_LEVEL_1 item code applies only to disks.
INIT$_NO_VERIFIED is the default for the following:
The INIT$_VERIFIED item codes apply only to disks.
The following diagram depicts the structure of the protection mask:

The default is the default protection of the caller.
For magnetic tape, the protection code is written to a specific volume label. The system applies only read and write access restrictions; execute and delete access are ignored. Moreover, the system and the owner are always given read and write access to magnetic tapes, regardless of the protection mask specified.
When you specify a protection mask for a disk volume, access type E (execute) indicates create access.
For Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 2 volumes, an initial security profile is created from the VOLUME.DEFAULT profile, with the owner and protection as currently defined for INITIALIZE.
You can use the $SET_SECURITY service to modify the security profile after the volume is initialized and mounted.
The caller needs read, write, or control access to the device.
When a file is opened, the file system uses the mapping pointers to access the data in the file.
The INIT$_WINDOW item code applies only to disks.
The INIT$_WRITECHECK item code applies only to disks.
The Initialize Volume system service formats a disk or magnetic tape volume and writes a label on the volume. At the end of initialization, the disk is empty except for the system files containing the structure information. All former contents of the volume are lost.A blank magnetic tape can sometimes cause unrecoverable errors when it is read. $INIT_VOL attempts to read the volume unless the following three conditions are in effect:
- INIT$_OVR_ACCESS Boolean item code is specified.
- INIT$_OVR_EXP Boolean item code is specified.
- Caller has VOLPRO privilege.
If the caller has VOLPRO privilege, $INIT_VOL initializes a disk without reading the ownership information; otherwise, the ownership of the volume is checked.A blank disk or a diskette with an incorrect format can sometimes cause a fatal drive error. Such a diskette can be initialized successfully by specifying the INIT$_DENSITY item code to format the diskette.
To initialize a particular volume, the caller must either have volume protection (VOLPRO) privilege or the volume must be one of the following:
- Blank disk or magnetic tape; that is, a volume that has never been written
- Disk that is owned by the caller's UIC or by the UIC [0,0]
- Magnetic tape that allows write access to the caller's UIC or that was not protected when it was initialized
None
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SET_SECURITY, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The item list or an address specified in the item list cannot be accessed. SS$_BADPARAM A buffer length of 0 was specified with a nonzero item code or an illegal item code was specified. SS$_IVSSRQ A concurrent call to SYS$INIT_VOL is already active for the process. SS$_NOPRIV The caller does not have sufficient privilege to initialize the volume. SS$_NOSUCHDEV The specified device does not exist on the host system. The $INIT_VOL service can also return the following condition values, which are specific to the Initialize Volume utility: INIT$_ALLOCFAIL Index file allocation failure. INIT$_BADACCESSED Value for INIT$_ACCESSED item code out of range. INIT$_BADBLOCKS Invalid syntax in bad block list. INIT$_BADCLUSTER Value for INIT$_CLUSTER_SIZE item code out of range. INIT$_BADDENS Invalid value for INIT$_DENSITY item code. INIT$_BADDIRECTORIES Value for INIT$_DIRECTORIES item code out of range. INIT$_BADEXTENSION Value for INIT$_EXTENSION item code out of range. INIT$_BADHEADERS Value for INIT$_HEADER item code out of range. INIT$_BADMAXFILES Value for INIT$_MAXFILES item code out of range. INIT$_BADOWNID Invalid value for owner ID. INIT$_BADRANGE Bad block address not on volume. INIT$_BADVOL1 Bad VOL1 ANSI label. INIT$_BADVOLACC Invalid value for INIT$_LABEL_ACCESS item code. INIT$_BADVOLLBL Invalid value for ANSI tape volume label. INIT$_BADWINDOWS Value for INIT$_WINDOWS item code out of range. INIT$_BLKZERO Block 0 is bad---volume not bootable. INIT$_CLUSTER Unsuitable cluster factor. INIT$_CONFQUAL Conflicting options were specified. INIT$_DIAGPACK Disk is a diagnostic pack. INIT$_ERASEFAIL Volume not completely erased. INIT$_FACTBAD Cannot read factory bad block data. INIT$_ILLOPT Item codes not appropriate for the device were specified. INIT$_INDEX Invalid index file position. INIT$_LARGECNT Disk too large to be supported. INIT$_MAXBAD Bad block table overflow. INIT$_MTLBLLONG Magnetic tape label specified is longer than 6 characters. INIT$_MTLBLNONA Magnetic tape label specified contains non-ANSI "a" characters. INIT$_NOBADDATA Bad block data not found on volume. INIT$_NONLOCAL Device is not a local device. INIT$_NOTRAN Logical name cannot be translated. INIT$_NOTSTRUC1 Options not available with Files-11 On-Disk Structure Level 1. INIT$_UNKDEV Unknown device type.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |