| Previous | Contents | Index |
The size of the returned bitmap is determined by the number of supported CPUs on the system. You can compute the number of bytes needed for the bitmap as follows: Use the $GETSYI system service with an item code of SYI$_MAX_CPUS to find the minimum number of bits needed, round this number up to a multiple of 64, and divide the result by 8.
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's powered set---those CPUs physically existing within the hard partition and powered up for operation.
The size of the returned bitmap is determined by the number of supported CPUs on the system. You can compute the number of bytes needed for the bitmap as follows: Use the $GETSYI system service with an item code of SYI$_MAX_CPUS to find the minimum number of bits needed, round this number up to a multiple of 64, and divide the result by 8.
On Alpha and I64 systems, returns a value that represents a CPU-indexed bitvector. When a particular bit position is set, the processor with that CPU ID value is a member of the instance's present set -- those CPUs physically existing within the hard partition. Being in the present set does not imply that it is part of the powered set.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, see the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, see the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, see the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
Note: OpenVMS support for RADs is available only on the AlphaServer GS series systems. For more information about using RADs, see the HP OpenVMS Alpha Partitioning and Galaxy Guide.
See the SYI$_CPUTYPE item code for a list of symbols and processors.
Because this number is a quadword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
On Alpha and I64 systems, SYI$_SID returns a value in which all fields are 0 except the CPU-type field, which always contains the value 256.
Because the value of this register is a longword hexadecimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
| Bit Position | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| KGB$V_DYNAMIC | Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. |
| KGB$V_NOACCESS | Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. |
| KGB$V_RESOURCE | Allows holders of an identifier to charge disk space to the identifier. It is used only for file objects. |
| KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM | Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. |
Allocate a buffer that is sufficient to hold the system rights list, because $GETSYI returns only as much of the list as will fit in the buffer.
Because SYI$_SYSTEM_UUID is 128 bits long, the buffer length field in the item descriptor must specify 16 bytes.
Because the version number is 8-byte blank-filled, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 8 (bytes).
You should obtain the general processor type value first by using the SYI$_CPU item code. For some of the general processor types, extended processor type information is provided by the item code, SYI$_XCPU. For other general processor types, the value returned by the SYI$_XCPU item code is currently undefined.
Because the processor type is a longword decimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
On VAX systems, the $PRDEF macro defines the following symbols for the extended processor types:
| VAX Processor Type Symbol |
Extended Processor Type |
Extended Processor Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| PR$_SID_TYPUV |
MicroVAX II
VAXstation II |
PR$_XSID_UV_UV2 |
|
MicroVAX 2000
VAXstation 2000 |
PR$_XSID_UV_410 | |
| PR$_SID_TYPCV | MicroVAX 3300, 3400, 3500, 3600, 3800, 3900 series | PR$_XSID_CV_650 |
| VAX 6000-200, 6000-300 series | PR$_XSID_CV_9CC | |
| VAXstation 3520, 3540 | PR$_XSID_CV_60 | |
| VAXstation 3100 series | PR$_XSID_CV_420 | |
| VAXft 3000 Model 310 | PR$_XSID_CV_520 | |
| PR$_SID_TYP8NN | VAX 8530 | PRS$_XSID_N8500 |
| VAX 8550 | PRS$_XSID_N8550 | |
| VAX 8810 (8700) | PRS$_XSID_N8700 | |
| VAX 8820-N (8800) | PRS$_XSID_N8800 | |
| PR$_SID_TYPRV | VAX 4000-300 | PR$_XSID_RV_670 |
| VAX 6000-400 series | PR$_XSID_RV_9RR |
Because the value of this register is a longword hexadecimal number, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
The buffer must specify a longword into which $GETSYI writes the value of the specified system parameter. For a list and description of all system parameters, see the HP OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
The Get Systemwide Information service returns information about the local system or about other systems in an OpenVMS Cluster configuration.None
This service uses the process's AST limit quota (ASTLM).
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The caller cannot read the item list, cannot write to the buffer specified by the buffer address field in an item descriptor, or cannot write to the return length address field in an item descriptor. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid item code. SS$_EXASTLM The process has exceeded its AST limit quota. SS$_NOMORENODE You requested a wildcard operation, and $GETSYI has returned information about all available nodes. SS$_NOSUCHNODE The specified node does not exist or is not currently a member of the OpenVMS Cluster system. SS$_UNREACHABLE Remote node is not currently reachable.
Same as those returned in R0.
/* Defining __NEW_STARLET enables the program to benefit from better type
checking for prototypes and structures provided by OpenVMS. */
#define __NEW_STARLET 1
#include <efndef> /* No Event Flag Event Flag */
#include <iledef> /* Item List Entry Definitions */
#include <iosbdef> /* I/O Status Block Structure Definition */
#include <starlet> /* Function Prototypes for System Services */
#include <stdio> /* C Standard I/O Functions */
#include <string> /* memset Prototype */
#include <syidef> /* $GETSYI Item Code Definitions */
#define NUM_ILE 3
#define BUFFER_SIZE 20
/* Macro to initialize a 32-bit item_list_3. */
#define init_ile32(ile, length, code, bufaddr, retlen_addr) \
{ (ile)->ile3$w_length = (length); \
(ile)->ile3$w_code = (code); \
(ile)->ile3$ps_bufaddr = (bufaddr); \
(ile)->ile3$ps_retlen_addr = (retlen_addr); }
/* Simple status checking macro. */
#define bad_status(status) (((status) & 1) != 1)
main ()
{
char
node_name [BUFFER_SIZE],
version_string [BUFFER_SIZE];
int
status;
unsigned short
node_name_length,
version_string_length;
ILE3
syi_ile [NUM_ILE];
IOSB
iosb;
/* Zeroing the item list has the effect of creating the terminating entry. */
memset (syi_ile, 0, ILE3$K_LENGTH*NUM_ILE);
/* Initialize the item list entries to fetch the operating system version
and the node name. */
init_ile32 (
&syi_ile [0],
BUFFER_SIZE,
SYI$_VERSION,
version_string,
&version_string_length);
init_ile32 (
&syi_ile [1],
BUFFER_SIZE,
SYI$_NODENAME,
node_name,
&node_name_length);
status = sys$getsyiw (
EFN$C_ENF,
NULL,
NULL,
&syi_ile,
&iosb,
NULL,
0);
if (bad_status (status)) return status;
if (bad_status (iosb.iosb$w_status)) return iosb.iosb$w_status;
/* Zero terminate the strings before displaying them. */
version_string [version_string_length] = '\0';
node_name [node_name_length] = '\0';
printf ("Version: %s Node Name: %s\n",
version_string,
node_name);
}
|
This example C program demonstrates how to use $GETSYIW to obtain the operating system version number string and the node name.
Returns information about the local system or about other systems in a cluster.The $GETSYIW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller with the requested information. For asynchronous completion, use the Get Systemwide Information ($GETSYI) service; $GETSYI returns to the caller after queuing the information request, without waiting for the information to be returned. In all other respects, these services are identical; For information about the $GETSYIW service, see the documentation about $GETSYI.
For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha and I64 systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$GETSYIW [efn] ,[csidadr] ,[nodename] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
int sys$getsyiw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *csidadr, void *nodename, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
You must specify either the csidadr or the nodename argument, but not both. For wildcard operations, however, you must use the csidadr argument.
Returns the current system time in a 64-bit format.On Alpha and I64 systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$GETTIM timadr
int sys$gettim (struct _generic_64 *timadr);
timadr
OpenVMS usage: date_time type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
The 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and I64 systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a quadword to receive the current time in 64-bit format.
The Get Time service returns the current system time in 64-bit format. The quadword is the number of nanoseconds since November 17, 1858. Based upon system time initialization, all bits in the time quadword are valid.On VAX systems, system time is updated every 10 milliseconds.
On Alpha and I64 systems, the frequency at which system time is updated varies, depending on the clock frequency of the Alpha or I64 processor, or approximately 1 millisecond.
None
None
$ASCTIM, $BINTIM, $CANTIM, $CANWAK, $NUMTIM, $SCHDWK, $SETIME, $SETIMR
For additional information about the system time, see the HP OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The quadword to receive the time cannot be written by the caller.
Returns authorization information about a specified user.
SYS$GETUAI [nullarg] ,[contxt] ,usrnam ,itmlst ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg] ,[nullarg]
int sys$getuai (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *contxt, void *usrnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
nullarg
OpenVMS usage: null_arg type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.contxt
OpenVMS usage: longword type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by reference
An optional longword used to maintain an open channel to the authorization file. The contxt argument is the address of a longword to receive a $GETUAI context value. If the contxt argument is specified on the initial call, this longword should contain the value --1, and on subsequent calls, the value of the contxt argument from the previous call should be passed back in.usrnam
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the user about whom $GETUAI returns authorization information. The usrnam argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character text string containing the user name. The user name string can contain a maximum of 12 alphanumeric characters.itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which information from the specified user's user authorization file (UAF) record is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of one or more item descriptors, each of which specifies an item code. The item list is terminated by an item code value of 0 or by a longword value of 0.The following diagram depicts the structure of a single item descriptor:
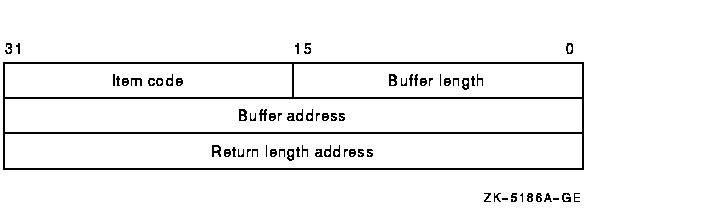
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETUAI is to write the information. The length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor, and is given in the description of each item code. If the value of the buffer length field is too small, $GETUAI truncates the data. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GETUAI is to return. The $UAIDEF macro defines these codes. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer in which $GETUAI is to write the information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which $GETUAI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually returned. |
The symbolic codes have the following format:
|
$UAI_code |
See the Item Codes section for descriptions of the various $GETUAI item codes.
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | nullarg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
UAI$_ACCOUNT
Returns, as a blank-filled 32-character string, the account name of the user.An account name can include up to 8 characters. Because the account name is a blank-filled string, however, the buffer length field of the item descriptor should specify 32 (bytes).
UAI$_ASTLM
Returns the AST queue limit.Because this decimal number is a word in length, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 2 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_P
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for primary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.The buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 3 (bytes).
UAI$_BATCH_ACCESS_S
Returns, as a 3-byte value, the range of times during which batch access is permitted for secondary days. Each bit set represents a 1-hour period, from bit 0 as midnight to 1 a.m. to bit 23 as 11 p.m. to midnight.
Previous Next Contents Index