| Previous | Contents | Index |
Deletes a Resource Manager instance (RMI) from the calling process.$FORGET_RMW always waits for the request to complete before returning to the caller. Other than this, it is identical to $FORGET_RM.
SYS$FORGET_RMW [efn] ,[flags] ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm] ,rm_id
int sys$forget_rmw (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, unsigned int rm_id);
Formats the specified access control entry (ACE) into a text string.
SYS$FORMAT_ACL aclent ,[acllen] ,aclstr ,[width] ,[trmdsc] ,[indent] ,[accnam] ,[nullarg]
int sys$format_acl (void *aclent, unsigned short int *acllen, void *aclstr, unsigned short int *width, void *trmdsc, unsigned short int *indent, unsigned int *accnam, int (*routin)(__unknown_params));
aclent
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Description of the ACE formatted when $FORMAT_ACL completes execution. The aclent argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a buffer containing the description of the input ACE. The first byte of the buffer contains the length of the ACE; the second byte contains a value that identifies the type of ACE, which in turn determines the ACE format.For more information about the ACE format, see the Description section.
acllen
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Length of the output string resulting when $FORMAT_ACL completes execution. The acllen argument is the address of a word containing the number of characters written to aclstr.aclstr
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Formatted ACE resulting when $FORMAT_ACL completes its execution. The aclstr argument is the address of a string descriptor pointing to a buffer containing the output string.width
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Maximum width of the formatted ACE resulting when $FORMAT_ACL completes its execution. The width argument is the address of a word containing the maximum width of the formatted ACE. If this argument is omitted or contains the value 0, an infinite length display line is assumed. When the width is exceeded, the character specified by trmdsc is inserted.trmdsc
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Line termination characters used in the formatted ACE. The trmdsc argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to a character string containing the termination characters that are inserted for each formatted ACE when the width has been exceeded.indent
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Number of blank characters beginning each line of the formatted ACE. The indent argument is the address of a word containing the number of blank characters that you want inserted at the beginning of each formatted ACE.accnam
OpenVMS usage: access_bit_names type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Names of the bits in the access mask when executing the $FORMAT_ACL. The accnam argument is the address of an array of 32 quadword descriptors that define the names of the bits in the access mask. Each element points to the name of a bit. The first element names bit 0, the second element names bit 1, and so on.You can call LIB$GET_ACCNAM to retrieve the access name table for the class of object whose ACL is to be formatted.
If you omit accnam, the following names are used:
Bit Name Bit 0 READ Bit 1 WRITE Bit 2 EXECUTE Bit 3 DELETE Bit 4 CONTROL Bit 5 BIT_5 Bit 6 BIT_6 .
.
.Bit 31 BIT_31 nullarg
OpenVMS usage: null_arg type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
The Format Access Control List Entry service formats the specified access control entry (ACE) into text string representation. There are seven types of ACE:
- Alarm ACE
- Application ACE
- Audit ACE
- Creator ACE
- Default Protection ACE
- Identifier ACE
- Subsystem ACE
The format for each of the ACE types is described in the following sections and the byte offsets and type values for each ACE type are defined in the $ACEDEF system macro library.
The access Alarm ACE generates a security alarm. Its format is as follows:
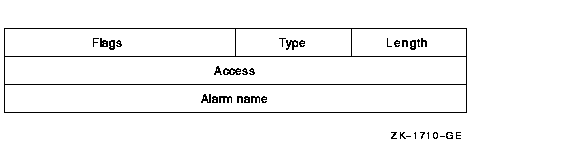
The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name for each:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ACE$B_SIZE | Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer |
| Type | ACE$B_TYPE | Byte containing the type value ACE$C_ALARM |
| Flags | ACE$W_FLAGS | Word containing Alarm ACE information and ACE type-independent information |
| Access | ACE$L_ACCESS | Longword containing a mask indicating the access modes to be watched |
| Alarm name | ACE$T_AUDITNAME | Character string containing the alarm name |
The flag field contains information specific to Alarm ACEs and information applicable to all types of ACEs. The following symbols are bit offsets to the Alarm ACE information:
| Bit Position | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_SUCCESS | Indicates that the alarm is raised when access is successful |
| ACE$V_FAILURE | Indicates that the alarm is raised when access fails |
The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is independent of ACE type:
| Bit Position | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_DEFAULT | This ACE is added to the ACL of any file created in the directory whose ACL contains this ACE. This bit is applicable only for an ACE in a directory file's ACL. |
| ACE$V_HIDDEN | This ACE is application dependent. You cannot use the DCL ACL commands and the ACL editor to change the setting; the DCL command DIRECTORY/ACL does not display it. |
| ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE | This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file. |
| ACE$V_PROTECTED | This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must delete this ACE explicitly. |
The following symbol values are offsets to bits within the access mask. You can also obtain the symbol values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the prefix ACE$M rather than ACE$V:
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_READ | Read access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_WRITE | Write access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_EXECUTE | Execute access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_DELETE | Delete access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_CONTROL | Modification of the access field is monitored. |
The Application ACE contains application-dependent information. Its format is as follows:
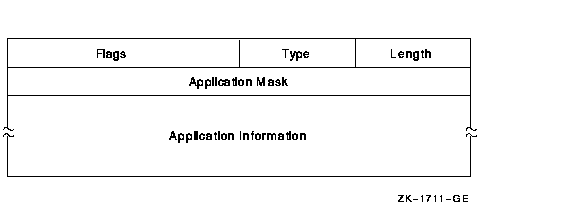
The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name for each:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ACE$B_SIZE | Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer. |
| Type | ACE$B_TYPE | Byte containing the type value ACE$C_INFO |
| Flags | ACE$W_FLAGS | Word containing Application ACE information and ACE type-independent information |
| Application mask | ACE$L_INFO_FLAGS | Longword containing a mask defined and used by the application |
| Application information | ACE$T_INFO_START | Variable-length data structure defined and used by the application. The length of this data is implied by the length field |
The flag field contains information specific to Application ACEs and information applicable to all types of ACEs. The following symbol is a bit offset to the Application ACE information:
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_INFO_TYPE | Four-bit field containing a value indicating whether the application is a CSS application (ACE$C_CSS) or a customer application (ACE$C_CUST). |
The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is independent of ACE type:
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_DEFAULT | This ACE is added to the ACL of any file created in the directory whose ACL contains this ACE. This bit is applicable only for an ACE in a directory file's ACL. |
| ACE$V_HIDDEN | This bit is application dependent. You cannot use the DCL ACL commands and the ACL editor to change the setting; the DCL command DIRECTORY/ACL does not display it. |
| ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE | This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file. |
| ACE$V_PROTECTED | This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must delete this ACE explicitly. |
The Audit ACE sets a security audit. Its format is as follows:

The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name for each:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ACE$B_SIZE | Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer |
| Type | ACE$B_TYPE | Byte containing the type value ACE$C_AUDIT |
| Flags | ACE$W_FLAGS | Word containing Audit ACE information and ACE type-independent information |
| Access | ACE$L_ACCESS | Longword containing a mask indicating the access modes to be watched |
| Alarm name | ACE$T_AUDITNAME | Character string containing the alarm name |
The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is independent of ACE type:
| Bit Position | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_DEFAULT | This ACE is added to the ACL of any file created in the directory whose ACL contains this ACE. This bit is applicable only for an ACE in a directory file's ACL. |
| ACE$V_HIDDEN | This ACE is application dependent. You cannot use the DCL ACL commands and the ACL editor to change the setting; the DCL command DIRECTORY/ACL does not display it. |
| ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE | This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file. |
| ACE$V_PROTECTED | This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must delete this ACE explicitly. |
The following symbol values are offsets to bits within the access mask. You can also obtain the symbol values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the prefix ACE$M rather than ACE$V.
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_READ | Read access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_WRITE | Write access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_EXECUTE | Execute access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_DELETE | Delete access is monitored. |
| ACE$V_CONTROL | Modification of the access field is monitored. |
The Creator ACE controls access to an object based on creators. Its format is as follows:
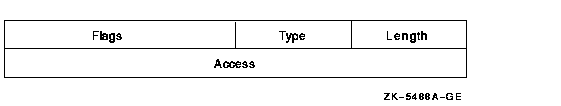
The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name for each:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ACE$B_SIZE | Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer. |
| Type | ACE$B_TYPE | Byte containing the type value ACE$C_NEW_OWNER. |
| Flags | ACE$W_FLAGS | Word containing Creator ACE information and ACE type-independent information. |
| Access | ACE$L_ACCESS | Longword containing a mask indicating the access modes to be granted to the creator of the file. |
The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is independent of ACE type:
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE | This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file. |
| ACE$V_PROTECTED | This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must delete this ACE explicitly. |
The following symbol values are offsets to bits within the mask indicating the access mode granted in the system, owner, group, and world fields:
| Bit Position | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_READ | Read access is granted. |
| ACE$V_WRITE | Write access is granted. |
| ACE$V_EXECUTE | Execute access is granted. |
| ACE$V_DELETE | Delete access is granted. |
| ACE$V_CONTROL | Modification of the access field is granted. |
You can also obtain the symbol values as masks with the appropriate bit set by using the prefix ACE$M rather than ACE$V.
The Default Protection ACE specifies the UIC-based protection for all files created in the directory. You can use this type of ACE only in the ACL of a directory file. Its format is as follows:
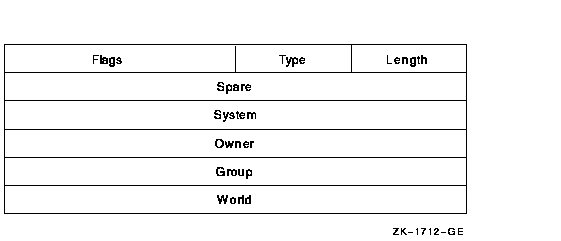
The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name for each:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ACE$B_SIZE | Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer. |
| Type | ACE$B_TYPE | Byte containing the type value ACE$C_DIRDEF. |
| Flags | ACE$W_FLAGS | Word containing ACE type-independent information. |
| Spare | ACE$L_SPARE1 | Longword that is reserved for future use and must be 0. |
| System | ACE$L_SYS_PROT | Longword containing a mask indicating the access mode granted to system users. Each bit represents one type of access. |
| Owner | ACE$L_OWN_PROT | Longword containing a mask indicating the access mode granted to the owner. Each bit represents one type of access. |
| Group | ACE$L_GRP_PROT | Longword containing a mask indicating the access mode granted to group users. Each bit represents one type of access. |
| World | ACE$L_WOR_PROT | Longword containing a mask indicating the access mode granted to the world. Each bit represents one type of access. |
The flag field contains information applicable to all types of ACEs. The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is independent of ACE type:
| Bit Position | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_HIDDEN | This ACE is application dependent. You cannot use the DCL ACL commands and the ACL editor to change the setting; the DCL command DIRECTORY/ACL does not display it. |
| ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE | This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file. |
| ACE$V_PROTECTED | This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must delete this ACE explicitly. |
The system interprets the bits within the access mask as shown in the following table. The following symbol values are offsets to bits within the mask indicating the access mode granted in the system, owner, group, and world fields:
| Bit Position | Meaning When Bit Is Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_READ | Read access is denied. |
| ACE$V_WRITE | Write access is denied. |
| ACE$V_EXECUTE | Execute access is denied. |
| ACE$V_DELETE | Delete access is denied. |
| ACE$V_CONTROL | Delete access is denied. |
You can also obtain the symbol values as masks with the appropriate bit set by using the prefix ACE$M rather than ACE$V.
The Identifier ACE controls access to an object based on identifiers. Its format is as follows:
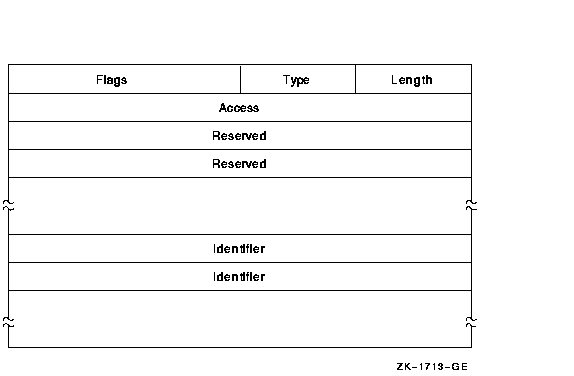
The following table describes the ACE fields and lists the symbol name for each:
| Field | Symbol Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Length | ACE$B_SIZE | Byte containing the length in bytes of the ACE buffer. |
| Type | ACE$B_TYPE | Byte containing the type value ACE$C_KEYID. |
| Flags | ACE$W_FLAGS | Word containing Identifier ACE information and ACE type-independent information. |
| Access | ACE$L_ACCESS | Longword containing a mask indicating the access mode granted to the specified identifiers. |
| Reserved | ACE$V_RESERVED | Longwords containing application-specific information. The number of reserved longwords is specified in the flags field. |
| Identifier | ACE$L_KEY | Longwords containing identifiers. The number of longwords is implied by ACE$B_SIZE. If an accessor holds all of the listed identifiers, the ACE is said to match the accessor, and the access specified in ACE$L_ACCESS is granted. |
The flags field contains information specific to Identifier ACEs and information applicable to all types of ACEs. The following symbol is a bit offset to Identifier ACE information:
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_RESERVED | Four-bit field containing the number of longwords to reserve for application-dependent data. The number must be between 0 and 15. The reserved longwords, if any, immediately precede the identifiers. |
The following symbols are bit offsets to ACE information that is independent of ACE type:
| Bit | Meaning When Set |
|---|---|
| ACE$V_DEFAULT | This ACE is added to the ACL of any file created in the directory whose ACL contains this ACE. This bit is applicable only for an ACE in a directory file's ACL. |
| ACE$V_HIDDEN | This bit is application dependent. You cannot use the DCL ACL commands and the ACL editor to change the setting; the DCL command DIRECTORY/ACL does not display it. |
| ACE$V_NOPROPAGATE | This ACE is not propagated among versions of the same file. |
| ACE$V_PROTECTED | This ACE is not deleted if the entire ACL is deleted; instead, you must delete this ACE explicitly. |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |